Metabolic signature of obesity-associated insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 31640727
- PMCID: PMC6805293
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-019-2096-8
Metabolic signature of obesity-associated insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Obesity is associated with an increased risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, some obese individuals maintain their insulin sensitivity and exhibit a lower risk of associated comorbidities. The underlying metabolic pathways differentiating obese insulin sensitive (OIS) and obese insulin resistant (OIR) individuals remain unclear.
Methods: In this study, 107 subjects underwent untargeted metabolomics of serum samples using the Metabolon platform. Thirty-two subjects were lean controls whilst 75 subjects were obese including 20 OIS, 41 OIR, and 14 T2DM individuals.
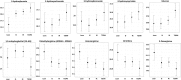
Results: Our results showed that phospholipid metabolites including choline, glycerophosphoethanolamine and glycerophosphorylcholine were significantly altered from OIS when compared with OIR and T2DM individuals. Furthermore, our data confirmed changes in metabolic markers of liver disease, vascular disease and T2DM, such as 3-hydroxymyristate, dimethylarginine and 1,5-anhydroglucitol, respectively.
Conclusion: This pilot data has identified phospholipid metabolites as potential novel biomarkers of obesity-associated insulin sensitivity and confirmed the association of known metabolites with increased risk of obesity-associated insulin resistance, with possible diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Further studies are warranted to confirm these associations in prospective cohorts and to investigate their functionality.
Keywords: Blood metabolites; Insulin resistance; Insulin sensitivity; Metabolomics; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bogers RP, Bemelmans WJ, Hoogenveen RT, Boshuizen HC, Woodward M, Knekt P, van Dam RM, Hu FB, Visscher TL, Menotti A, et al. Association of overweight with increased risk of coronary heart disease partly independent of blood pressure and cholesterol levels: a meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies including more than 300 000 persons. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:1720–1728. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.16.1720. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

