Transcriptome-Based Prediction of Complex Traits in Maize
- PMID: 31641024
- PMCID: PMC6961623
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.19.00332
Transcriptome-Based Prediction of Complex Traits in Maize
Abstract
The ability to predict traits from genome-wide sequence information (i.e., genomic prediction) has improved our understanding of the genetic basis of complex traits and transformed breeding practices. Transcriptome data may also be useful for genomic prediction. However, it remains unclear how well transcript levels can predict traits, particularly when traits are scored at different development stages. Using maize (Zea mays) genetic markers and transcript levels from seedlings to predict mature plant traits, we found that transcript and genetic marker models have similar performance. When the transcripts and genetic markers with the greatest weights (i.e., the most important) in those models were used in one joint model, performance increased. Furthermore, genetic markers important for predictions were not close to or identified as regulatory variants for important transcripts. These findings demonstrate that transcript levels are useful for predicting traits and that their predictive power is not simply due to genetic variation in the transcribed genomic regions. Finally, genetic marker models identified only 1 of 14 benchmark flowering-time genes, while transcript models identified 5. These data highlight that, in addition to being useful for genomic prediction, transcriptome data can provide a link between traits and variation that cannot be readily captured at the sequence level.
© 2020 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures
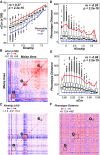



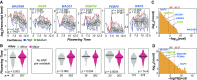
Comment in
-
Predicting Adult Complex Traits from Early Development Transcript Data in Maize.Plant Cell. 2020 Jan;32(1):10-11. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00833. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 31649124 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Albert F.W., Kruglyak L. (2015). The role of regulatory variation in complex traits and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 16: 197–212. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury P.J., Zhang Z., Kroon D.E., Casstevens T.M., Ramdoss Y., Buckler E.S. (2007). TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23: 2633–2635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

