Nonfunctioning and Subclinical Cortisol Secreting Adrenal Incidentalomas and their Association with Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 31641636
- PMCID: PMC6683688
- DOI: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_52_19
Nonfunctioning and Subclinical Cortisol Secreting Adrenal Incidentalomas and their Association with Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: A growing body of evidence suggests that nonfunctioning and subclinical cortisol secreting adrenal incidentalomas (AIs) are associated with several components of metabolic syndrome resulting in increased cardiometabolic risk. The long-term metabolic outcome of these AIs is largely unknown and their most appropriate management remains controversial.
Objectives: To undertake a systematic review of the prevalence of cardiometabolic abnormalities in nonfunctioning and subclinical cortisol secreting AIs and long-term outcome of conservative treatment and adrenalectomy.
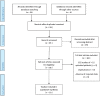
Methods: MEDLINE, Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, and EMBASE were searched for relevant studies and systematic review was performed. National Institutes of Health (NIH) quality assessment tool for observational cohort and cross-sectional studies was used to assess the risk of bias in the studies.
Results: Of the 65 studies screened, 18 (10 retrospective, 5 prospective, 2 cross-sectional studies, and 1 randomized controlled trial) were included in the systematic review. Prevalence of hypertension (HTN), impaired glucose metabolism, dyslipidaemia, and raised body mass index (BMI) was higher in subclinical cortisol secreting AIs as compared with nonfunctioning AIs. Surgical intervention had a beneficial effect on blood pressure, glucometabolic control, and obesity in patients with subclinical Cushing's syndrome. The results for lipid metabolism were equivocal. There was no significant improvement in cardiometabolic risk factors after adrenalectomy in nonfunctioning AIs. The quality of evidence was found to be low to moderate.
Conclusions: The systematic review demonstrated increased prevalence of components of metabolic syndrome in patients with subclinical cortisol secreting and nonfunctioning AIs. A beneficial role of adrenalectomy on HTN, glucometabolic control, and BMI was observed in patients with subclinical cortisol secreting AIs.
Keywords: Adrenal incidentalomas; metabolic syndrome; subclinical Cushing's syndrome; systematic review.
Copyright: © 2019 Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peppa M, Boutati E, Koliaki C, Papaefstathiou N, Garoflos E, Economopoulos T, et al. Insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome in patients with nonfunctioning adrenal incidentalomas: A cause-effect relationship? Metabolism. 2010;59:1435–41. - PubMed
-
- Terzolo M, Pia A, Ali A, Osella G, Reimondo G, Bovio S, et al. Adrenal incidentaloma: A new cause of the metabolic syndrome? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:998–1003. - PubMed
-
- Zhang W, Tang ZY, Wang WQ, Ning G. Metabolic syndrome inpatients with adrenocortical adenoma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006;86:3397–400. - PubMed
-
- Peppa M, Koliaki C, Raptis SA. Adrenal incidentalomas and cardiometabolic morbidity: An emerging association with serious clinical implications. J Intern Med. 2010;268:555–66. - PubMed
-
- Reincke M, Fassnacht M, Vath S, Mora P, Allolio B. Adrenal incidentalomas: A manifestation of the metabolic syndrome? Endocr Res. 1996;22:757–61. - PubMed