Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: More than Just a Colonizer!
- PMID: 31645832
- PMCID: PMC6775712
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23241
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: More than Just a Colonizer!
Abstract
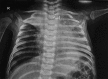
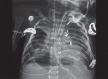
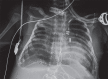
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is an emerging gram-negative pathogen that was previously labeled as a colonizer. Nowadays, with multiple antibiotic usage along with certain host factors, infections caused by this organism are getting attention. We hereby report two cases of ventilator-associated pneumonia in postoperative infants by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in a cardiac intensive care unit (ICU). How to cite this article: Baidya A, Kodan P, Fazal F, Tsering S, Menon RP, Jorwal P, et al. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: More than Just a Colonizer! Indian J Crit Care Med 2019;23(9):434-436.
Keywords: Nosocomial; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; Ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Copyright © 2019; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Muder RR, Yu VL, Dummer JS, Vinson C, Lumish RM. Infections caused by Pseudomonas maltophilia: expanding clinical spectrum. Arch Intern Med. 1987;147:1672–1674. - PubMed
-
- Gopalakrishnan R, Hawley HB, Czachor JS, Markert RJ, Bernstein JM. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infection and colonization in the intensive care unit of two community hospitals: a study of 143 patients. Heart Lung. 1999;28:134–141. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources