Nivolumab-related severe thrombocytopenia in a patient with relapsed lung adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 31647029
- PMCID: PMC6813076
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-019-2245-y
Nivolumab-related severe thrombocytopenia in a patient with relapsed lung adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy has changed the standard drug therapy for relapsed or advanced non-small cell lung cancer; its efficacy is well-recognized by pulmonary physicians, oncologists, and thoracic surgeons. Nivolumab, one of the anti-programmed cell death 1 antibodies, was the first immune checkpoint inhibitor to be approved and is used as a standard second-line regimen for patients with non-small cell lung cancer irrespective of the expression of programmed cell death ligand 1. Programmed cell death 1 antibodies have been generally confirmed to be less toxic than conventional cytotoxic chemotherapy, although unusual immune-related adverse events such as type I diabetes mellitus, adrenal failure, and myasthenia gravis may occur with a very low incidence. A case of severe grade V immune-related thrombocytopenia after two courses of nivolumab as second-line therapy for relapsed non-small cell lung cancer is reported.
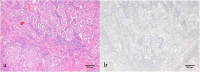
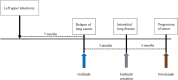
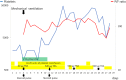
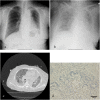
Case presentation: An 82-year-old Japanese woman with relapsed lung adenocarcinoma was treated with nivolumab as second-line systemic therapy at our institute. Her laboratory data indicated thrombocytopenia suspected to be an immune-related adverse event following two courses of nivolumab. Subsequently, she developed a massive pulmonary hemorrhage and left cerebral infarction despite intensive treatment including systemic steroid therapy. Although there have been a few reports of thrombocytopenia caused by nivolumab, this is the first report of grade V thrombocytopenia following administration of nivolumab for relapsed non-small cell lung cancer.
Conclusion: A very difficult case of grade V immune-related thrombocytopenia after the administration of nivolumab as second-line therapy for relapsed lung adenocarcinoma was described. Immune-related thrombocytopenia is a rare adverse event, but it must be considered a possible complication because it may become critical once it has occurred.
Keywords: Immune checkpoint inhibitor; Immune-related thrombocytopenia; Nivolumab; Non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency and thyroiditis associated with nivolumab therapy in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2019 Mar 26;13(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13256-019-2002-2. J Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30909965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nivolumab in chemotherapy-resistant cervical cancer: report of a vulvitis as a novel immune-related adverse event and molecular analysis of a persistent complete response.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Oct 31;7(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0742-6. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31672171 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab-induced severe pancytopenia in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma.Lung Cancer. 2018 May;119:21-24. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.02.018. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29656748
-
Thrombocytopenia in patients with melanoma receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2017 Feb 21;5:8. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0210-0. eCollection 2017. J Immunother Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28239462 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab-Induced Polymyalgia Rheumatica in a Patient with Lung Adenocarcinoma.Am J Med Sci. 2021 Sep;362(3):321-323. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2021.04.010. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Am J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33905737 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune thrombocytopenia in a small cell lung cancer patient treated with atezolizumab: a case report.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Nov;11(11):2346-2355. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-745. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36519029 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab-induced immune thrombocytopenia in a patient with malignant pleural mesothelioma.Respir Med Case Rep. 2020 Jul 17;31:101170. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101170. eCollection 2020. Respir Med Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32714828 Free PMC article.
-
[Immune Thrombocytopenia Induced by Sintilimab in Lung Cancer: A Case Report and Literature Review].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2023 Sep 20;26(9):717-720. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.102.32. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37985158 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Immune Thrombocytopenia Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitrs in Lung Cancer: Case Report and Literature Review.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 9;12:790051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.790051. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34956221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acquired amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia after durvalumab administration.J Clin Exp Hematop. 2021 Mar 18;61(1):53-57. doi: 10.3960/jslrt.20047. Epub 2021 Jan 8. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2021. PMID: 33431742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, Park K, Ciardiello F, von Pawel J, Gadgeel SM, Hida T, Kowalski DM, Dols MC, et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:255–265. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32517-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

