High rate of durable complete remission in follicular lymphoma after CD19 CAR-T cell immunotherapy
- PMID: 31648294
- PMCID: PMC6695558
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019000905
High rate of durable complete remission in follicular lymphoma after CD19 CAR-T cell immunotherapy
Abstract
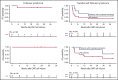
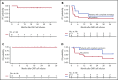
Patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) with early relapse after initial chemoimmunotherapy, refractory disease, or histologic transformation (tFL) have limited progression-free and overall survival. We report efficacy and long-term follow-up of 21 patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) FL (n = 8) and tFL (n = 13) treated on a phase 1/2 clinical trial with cyclophosphamide and fludarabine lymphodepletion followed by infusion of 2 × 106 CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor-modified T (CAR-T) cells per kilogram. The complete remission (CR) rates by the Lugano criteria were 88% and 46% for patients with FL and tFL, respectively. All patients with FL who achieved CR remained in remission at a median follow-up of 24 months. The median duration of response for patients with tFL was 10.2 months at a median follow-up of 38 months. Cytokine release syndrome occurred in 50% and 39%, and neurotoxicity in 50% and 23% of patients with FL and tFL, respectively, with no severe adverse events (grade ≥3). No significant differences in CAR-T cell in vivo expansion/persistence were observed between FL and tFL patients. CD19 CAR-T cell immunotherapy is highly effective in adults with clinically aggressive R/R FL with or without transformation, with durable remission in a high proportion of FL patients. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01865617.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: K.A.H. has served on advisory boards for Celgene; S.R.R. holds equity, has served as an advisor, and has patents licensed to Juno Therapeutics, a Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb company; is a founder of Lyell Immunopharma; and has served on advisory boards for Adaptive Biotechnologies and Nohla; D.G.M. has received research funding from Kite Pharma, a Gilead Company, Juno Therapeutics, a Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb company, and Celgene; has served on advisory boards for Kite Pharma, Gilead, Genentech, Novartis, and Eureka Therapeutics; C.J.T. receives research funding from Juno Therapeutics, a Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb company, and Nektar Therapeutics; has patents licensed to Juno Therapeutics, a Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb company; has served on advisory boards and has equity ownership in Caribou Biosciences, Eureka Therapeutics, and Precision Biosciences; and has served on advisory boards for Aptevo, Juno Therapeutics, a Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb company, Kite Pharma, a Gilead Company, Humanigen, Nektar Therapeutics, Allogene, and Novartis. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
CAR T-cell Therapy Yields Durable Remissions in FL.Cancer Discov. 2019 Sep;9(9):OF4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2019-082. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Cancer Discov. 2019. PMID: 31332022
-
The case for CAR T-cell therapy in follicular lymphomas.Blood. 2019 Aug 15;134(7):577-578. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001843. Blood. 2019. PMID: 31416814 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, et al. ; JULIET Investigators. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45-56. - PubMed
-
- Casulo C, Byrtek M, Dawson KL, et al. . Early relapse of follicular lymphoma after rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone defines patients at high risk for death: an analysis from the National LymphoCare Study [published correction appears in J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(12):1430]. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(23):2516-2522. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rivas-Delgado A, Magnano L, Moreno-Velázquez M, et al. . Response duration and survival shorten after each relapse in patients with follicular lymphoma treated in the rituximab era. Br J Haematol. 2019;184(5):753-759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

