Understanding childhood obesity in the US: the NIH environmental influences on child health outcomes (ECHO) program
- PMID: 31649277
- PMCID: PMC7060502
- DOI: 10.1038/s41366-019-0470-5
Understanding childhood obesity in the US: the NIH environmental influences on child health outcomes (ECHO) program
Abstract
Background: Few resources exist for prospective, longitudinal analysis of the relationships between early life environment and later obesity in large diverse samples of children in the United States (US). In 2016, the National Institutes of Health launched the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) program to investigate influences of environmental exposures on child health and development. We describe demographics and overweight and obesity prevalence in ECHO, and ECHO's potential as a resource for understanding how early life environmental factors affect obesity risk.
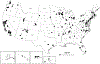
Methods: In this cross-sectional study of 70 extant US and Puerto Rico cohorts, 2003-2017, we examined age, race/ethnicity, and sex in children with body mass index (BMI) data, including 28,507 full-term post-birth to <2 years and 38,332 aged 2-18 years. Main outcomes included high BMI for age <2 years, and at 2-18 years overweight (BMI 85th to <95th percentile), obesity (BMI ≥ 95th percentile), and severe obesity (BMI ≥ 120% of 95th percentile).
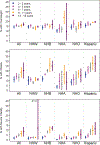
Results: The study population had diverse race/ethnicity and maternal demographics. Each outcome was more common with increasing age and varied with race/ethnicity. High BMI prevalence (95% CI) was 4.7% (3.5, 6.0) <1 year, and 10.6% (7.4, 13.7) for 1 to <2 years; overweight prevalence increased from 13.9% (12.4, 15.9) at 2-3 years to 19.9% (11.7, 28.2) at 12 to <18 years. ECHO has the statistical power to detect relative risks for 'high' BMI ranging from 1.2 to 2.2 for a wide range of exposure prevalences (1-50%) within each age group.
Conclusions: ECHO is a powerful resource for understanding influences of chemical, biological, social, natural, and built environments on onset and trajectories of obesity in US children. The large sample size of ECHO cohorts adopting a standardized protocol for new data collection of varied exposures along with longitudinal assessments will allow refined analyses to identify drivers of childhood obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kumar S, Kelly AS. Review of childhood obesity: from epidemiology, etiology, and comorbidities to clinical assessment and treatment. Mayo Clinic Proc. 2017;92:251–65. - PubMed
-
- Hanson MA, Gluckman PD. Developmental origins of health and disease-global public health implications. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2015;29:24–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UG1 HD090899/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023275/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023286/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023271/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK111022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023282/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023347/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023305/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD034568/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023285/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023382/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023289/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023249/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023290/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023287/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023285/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023320/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023248/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD030016/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL141589/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023282/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023271/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK120807/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023305/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES022832/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK092924/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023286/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023289/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023316/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023320/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024949/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023249/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023290/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD035516/OD/NIH HHS/United States

