Determining Immune and miRNA Biomarkers Related to Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Types
- PMID: 31649663
- PMCID: PMC6794384
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02323
Determining Immune and miRNA Biomarkers Related to Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Types
Abstract
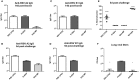
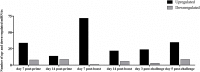
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) causes serious respiratory tract illness and substantial morbidity and some mortality in populations at the extremes of age, i.e., infants, young children, and the elderly. To date, RSV vaccine development has been unsuccessful, a feature linked to the lack of biomarkers available to assess the safety and efficacy of RSV vaccine candidates. We examined microRNAs (miR) as potential biomarkers for different types of RSV vaccine candidates. In this study, mice were vaccinated with a live attenuated RSV candidate that lacks the small hydrophobic (SH) and attachment (G) proteins (CP52), an RSV G protein microparticle (GA2-MP) vaccine, a formalin-inactivated RSV (FI-RSV) vaccine or were mock-treated. Several immunological endpoints and miR expression profiles were determined in mouse serum and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) following vaccine priming, boost, and RSV challenge. We identified miRs that were linked with immunological parameters of disease and protection. We show that miRs are potential biomarkers providing valuable insights for vaccine development.
Keywords: RSV; disease; immune; miR; microRNA; vaccines.
Copyright © 2019 Atherton, Jorquera, Bakre and Tripp.
Figures

References
-
- Shi T, McAllister DA, O'Brien KL, Simoes EAF, Madhi SA, Gessner BD, et al. . Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: a systematic review and modelling study. Lancet. (2017) 390:946–58. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30938-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

