A chronological map of 308 physical and mental health conditions from 4 million individuals in the English National Health Service
- PMID: 31650125
- PMCID: PMC6798263
- DOI: 10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30012-3
A chronological map of 308 physical and mental health conditions from 4 million individuals in the English National Health Service
Abstract
Background: To effectively prevent, detect, and treat health conditions that affect people during their lifecourse, health-care professionals and researchers need to know which sections of the population are susceptible to which health conditions and at which ages. Hence, we aimed to map the course of human health by identifying the 50 most common health conditions in each decade of life and estimating the median age at first diagnosis.
Methods: We developed phenotyping algorithms and codelists for physical and mental health conditions that involve intensive use of health-care resources. Individuals older than 1 year were included in the study if their primary-care and hospital-admission records met research standards set by the Clinical Practice Research Datalink and they had been registered in a general practice in England contributing up-to-standard data for at least 1 year during the study period. We used linked records of individuals from the CALIBER platform to calculate the sex-standardised cumulative incidence for these conditions by 10-year age groups between April 1, 2010, and March 31, 2015. We also derived the median age at diagnosis and prevalence estimates stratified by age, sex, and ethnicity (black, white, south Asian) over the study period from the primary-care and secondary-care records of patients.
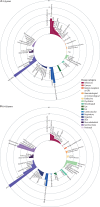
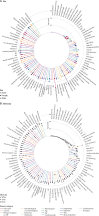
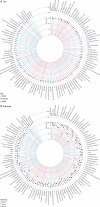
Findings: We developed case definitions for 308 disease phenotypes. We used records of 2 784 138 patients for the calculation of cumulative incidence and of 3 872 451 patients for the calculation of period prevalence and median age at diagnosis of these conditions. Conditions that first gained prominence at key stages of life were: atopic conditions and infections that led to hospital admission in children (<10 years); acne and menstrual disorders in the teenage years (10-19 years); mental health conditions, obesity, and migraine in individuals aged 20-29 years; soft-tissue disorders and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in individuals aged 30-39 years; dyslipidaemia, hypertension, and erectile dysfunction in individuals aged 40-59 years; cancer, osteoarthritis, benign prostatic hyperplasia, cataract, diverticular disease, type 2 diabetes, and deafness in individuals aged 60-79 years; and atrial fibrillation, dementia, acute and chronic kidney disease, heart failure, ischaemic heart disease, anaemia, and osteoporosis in individuals aged 80 years or older. Black or south-Asian individuals were diagnosed earlier than white individuals for 258 (84%) of the 308 conditions. Bone fractures and atopic conditions were recorded earlier in male individuals, whereas female individuals were diagnosed at younger ages with nutritional anaemias, tubulointerstitial nephritis, and urinary disorders.
Interpretation: We have produced the first chronological map of human health with cumulative-incidence and period-prevalence estimates for multiple morbidities in parallel from birth to advanced age. This can guide clinicians, policy makers, and researchers on how to formulate differential diagnoses, allocate resources, and target research priorities on the basis of the knowledge of who gets which diseases when. We have published our phenotyping algorithms on the CALIBER open-access Portal which will facilitate future research by providing a curated list of reusable case definitions.
Funding: Wellcome Trust, National Institute for Health Research, Medical Research Council, Arthritis Research UK, British Heart Foundation, Cancer Research UK, Chief Scientist Office of the Scottish Government Health and Social Care Directorates, Department of Health and Social Care (England), Health and Social Care Research and Development Division (Welsh Government), Public Health Agency (Northern Ireland), Economic and Social Research Council, Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, National Institute for Social Care and Health Research, and The Alan Turing Institute.
© 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license.
Figures






Comment in
-
Depicting the spectrum of diseases that occur during the lifespan of an individual based on electronic health records.Lancet Digit Health. 2019 Jun;1(2):e46-e47. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30023-8. Epub 2019 May 20. Lancet Digit Health. 2019. PMID: 33323226 No abstract available.
References
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnett K, Mercer S, Norbury M, Watt G, Wyke S, Guthrie B. The epidemiology of multimorbidity in a large cross-sectional dataset: implications for health care, research and medical education. Lancet. 2012;380:37–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

