Urinary Biomarkers may Complement the Cleveland Score for Prediction of Adverse Kidney Events After Cardiac Surgery: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 31650729
- PMCID: PMC6822001
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.2.131
Urinary Biomarkers may Complement the Cleveland Score for Prediction of Adverse Kidney Events After Cardiac Surgery: A Pilot Study
Abstract
Background: The ability of urinary biomarkers to complement established clinical risk prediction models for postoperative adverse kidney events is unclear. We assessed the effect of urinary biomarkers linked to suspected pathogenesis of cardiac surgery-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) on the performance of the Cleveland Score, a risk assessment model for postoperative adverse kidney events.
Methods: This pilot study included 100 patients who underwent open-heart surgery. We determined improvements to the Cleveland Score when adding urinary biomarkers measured using clinical laboratory platforms (neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin [NGAL], interleukin-6) and those in the preclinical stage (hepcidin-25, midkine, alpha-1 microglobulin), all sampled immediately post-surgery. The primary endpoint was major adverse kidney events (MAKE), and the secondary endpoint was AKI. We performed ROC curve analysis, assessed baseline model performance (odds ratios [OR], 95% CI), and carried out statistical reclassification analyses to assess model improvement.
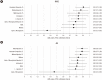
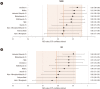
Results: NGAL (OR [95% CI] per 20 concentration-units wherever applicable): (1.07 [1.01-1.14]), Interleukin-6 (1.51 [1.01-2.26]), midkine (1.01 [1.00-1.02]), 1-hepcidin-25 (1.08 [1.00-1.17]), and NGAL/hepcidin-ratio (2.91 [1.30-6.49]) were independent predictors of MAKE and AKI (1.38 [1.03-1.85], 1.08 [1.01-1.15], 1.01 [1.00-1.02], 1.09 [1.01-1.18], and 3.45 [1.54-7.72]). Category-free net reclassification improvement identified interleukin-6 as a model-improving biomarker for MAKE and NGAL for AKI. However, only NGAL/hepcidin-25 improved model performance for event- and event-free patients for MAKE and AKI.
Conclusions: NGAL and interleukin-6 measured immediately post cardiac surgery may complement the Cleveland Score. The combination of biomarkers with hepcidin-25 may further improve diagnostic discrimination.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Cardiac surgery; Cleveland Score; Hepcidin; Interleukin-6; Major adverse kidney events; Midkine; Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; Reclassification analysis.
© The Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
CA has received honoraria speaking for Siemens Healthineers. MH has received honoraria speaking for Abbott Diagnostics, Alere, Biosite Inc., and Siemens Healthineers, AA has received honoraria speaking for Abbott Diagnostics. All companies are involved in the development and marketing of renal biomarkers.
Figures


Comment in
-
Hepcidin and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as a Biomarker for Acute Kidney Injury Linked Iron Metabolism.Ann Lab Med. 2020 Mar;40(2):97-98. doi: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.2.97. Ann Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 31650724 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Haase-Fielitz A, Haase M, Bellomo R, Calzavacca P, Spura A, Baraki H, et al. Perioperative hemodynamic instability and fluid overload are associated with increasing acute kidney injury severity and worse outcome after cardiac surgery. Blood Purif. 2017;43:298–308. - PubMed
-
- Kellum JA, Lameire N, Aspelin P, Barsoum RS, Burdmann EA, Goldstein SL, et al. Kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2:1–138.
-
- Thakar CV, Arrigain S, Worley S, Yared JP, Paganini EP. A clinical score to predict acute renal failure after cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Vives M, Monedero P, Perez-Valdivieso JR, Garcia-Fernandez N, Lavilla J, Herreros J, et al. External validation and comparison of three scores to predict renal replacement therapy after cardiac surgery: a multicenter cohort. Int J Artif Organs. 2011;34:329–338. - PubMed
-
- McCullough PA, Shaw AD, Haase M, Bouchard J, Waikar SS, Siew ED, et al. Diagnosis of acute kidney injury using functional and injury biomarkers: workgroup statements from the tenth Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Consensus Conference. Contrib Nephrol. 2013;182:13–29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

