Understanding biochemistry: structure and function of nucleic acids
- PMID: 31652314
- PMCID: PMC6822018
- DOI: 10.1042/EBC20180038
Understanding biochemistry: structure and function of nucleic acids
Abstract
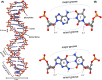
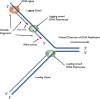
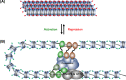
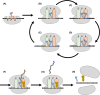
Nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), carry genetic information which is read in cells to make the RNA and proteins by which living things function. The well-known structure of the DNA double helix allows this information to be copied and passed on to the next generation. In this article we summarise the structure and function of nucleic acids. The article includes a historical perspective and summarises some of the early work which led to our understanding of this important molecule and how it functions; many of these pioneering scientists were awarded Nobel Prizes for their work. We explain the structure of the DNA molecule, how it is packaged into chromosomes and how it is replicated prior to cell division. We look at how the concept of the gene has developed since the term was first coined and how DNA is copied into RNA (transcription) and translated into protein (translation).
Keywords: Concept of the gene; DNA Replication; Nucleic acids; Transcription; Translation.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures










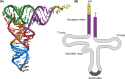


References
Recommended reading and key publications: Nobel lectures
-
- Blackburn E.H. (2010) Telomeres and Telomerase: The Means to the End (Nobel Lecture) 49, Int. Ed., pp. 7405–7421, Angewandte Chemie - PubMed
-
- Ehrenberg M. (2009) Scientific Background on the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009 Structure and Function of the Ribosome, The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, https://www.nobelprize.org/uploads/2018/06/advanced-chemistryprize2009.pdf
-
- Kornberg R.D. (2007) The Molecular Basis of Eukaryotic Transcription (Nobel Lecture) 32, Int. Ed., pp. 12955–12961, Angewandte Chemie - PubMed
Review articles
-
- Minchin S.D. and Busby S.J.W. (2013) Transcription factors. In Brenner’s Encyclopedia of Genetics(Maloy S. and Hughes K., eds), Elsevier, U.S.A.
Historical perspectives
-
- Maddox B. (2003) The double helix and the “wronged heroine”. Nature 421, 407–408 - PubMed
Original research papers
Citations for figures
-
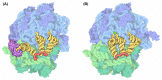
- Goodsell D. (2010) Molecule of the month: ribosome. https://pdb101.rcsb.org/motm/121
-
- Yikrazuul X.X. (2010) tRNA-Phe yeast. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:TRNA-Phe_yeast_1ehz.png
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

