Efficient Gene Disruption via Base Editing Induced Stop in Newt Pleurodeles waltl
- PMID: 31652881
- PMCID: PMC6895984
- DOI: 10.3390/genes10110837
Efficient Gene Disruption via Base Editing Induced Stop in Newt Pleurodeles waltl
Abstract
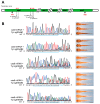
Loss-of-function approaches provide strong evidence for determining the role of particular genes. The prevalent CRISPR/Cas9 technique is widely used to disrupt target gene with uncontrolled non-homologous end joining after the double strand breaks, which results in mosaicism and multiple genotypes in the founders. In animal models with long generation time such as the salamanders, producing homozygous offspring mutants would be rather labor intensive and time consuming. Here we utilized the base editing technique to create the loss-of-function F0 mutants without the random indels. As a proof of principle, we successfully introduced premature stop codons into the tyrosinase locus and produced the albino phenotype in the newts (Pleurodeles waltl). We further demonstrated that the knockout efficiency could be greatly improved by using multiplex sgRNAs target the same gene. The F0 mutated animals showed fully loss-of-function by both genotyping and phenotyping analysis, which could enable direct functional analysis in the founders and avoid sophisticated breeding. This study not only presented the high efficiency of single base editing in a gigantic animal genome (>20 G), but also provided new tools for interrogating gene function in other salamander species.
Keywords: base editing; genome; newt; sgRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Pasmans F., Martel A. Mader’s Reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. Amphibian Taxonomy, Anatomy, and Physiology; pp. 86–89.
-
- Brockes J.P. Salamanders in Regeneration Research. Humana Press; New York, NY, USA: 2015. Variation in Salamanders: An Essay on Genomes, Development, and Evolution; pp. 3–15. - PubMed
-
- Elewa A., Wang H., Talavera-López C., Joven A., Brito G., Kumar A., Hameed L.S., Penrad-Mobayed M., Yao Z., Zamani N., et al. Reading and editing the Pleurodeles waltl genome reveals novel features of tetrapod regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:2286. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01964-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

