Galeterone and The Next Generation Galeterone Analogs, VNPP414 and VNPP433-3β Exert Potent Therapeutic Effects in Castration-/Drug-Resistant Prostate Cancer Preclinical Models In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 31653008
- PMCID: PMC6895912
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11111637
Galeterone and The Next Generation Galeterone Analogs, VNPP414 and VNPP433-3β Exert Potent Therapeutic Effects in Castration-/Drug-Resistant Prostate Cancer Preclinical Models In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
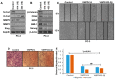
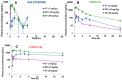
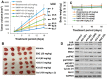
These studies compared the efficacies of our clinical agent galeterone (Gal) and the FDA-approved prostate cancer drug, enzalutamide (ENZ) with two lead next generation galeterone analogs (NGGAs), VNPP414 and VNPP433-3β, using prostate cancer (PC) in vitro and in vivo models. Antitumor activities of orally administered agents were also assessed in CWR22Rv1 tumor-bearing mice. We demonstrated that Gal and NGGAs degraded AR/AR-V7 and Mnk1/2; blocked cell cycle progression and proliferation of human PC cells; induced apoptosis; inhibited cell migration, invasion, and putative stem cell markers; and reversed the expression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). In addition, Gal/NGGAs (alone or in combination) also inhibited the growth of ENZ-, docetaxel-, and mitoxantrone-resistant human PC cell lines. The NGGAs exhibited improved pharmacokinetic profiles over Gal in mice. Importantly, in vivo testing showed that VNPP433-3β (at 7.53-fold lower equimolar dose than Gal) markedly suppressed (84% vs. Gal, 47%; p < 0.01) the growth of castration-resistant PC (CRPC) CWR22Rv1 xenograft tumors, with no apparent host toxicity. ENZ was ineffective in this CRPC xenograft model. In summary, our findings show that targeting AR/AR-V7 and Mnk1/2 for degradation represents an effective therapeutic strategy for PC/CRPC treatment and supports further development of VNPP433-3β towards clinical investigation.
Keywords: Mnk-eIF4E/mTORC1 signaling pathways; Mnk1/2 degraders; NGGAs; VNPP433-3β AR/AR-V7; apoptosis; castration-/drug-resistant PC cell; galeterone (Gal); prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Vincent C. O. Njar is the lead inventor of galeterone and the NGGAs, the patents and technologies thereof are owned by the University of Maryland, Baltimore. Puranik Purushottamachar and Francis N. Murigi are co-inventors of the NGGAs. The other authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel AR/AR-V7 and Mnk1/2 Degrader, VNPP433-3β: Molecular Mechanisms of Action and Efficacy in AR-Overexpressing Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo Models.Cells. 2022 Aug 30;11(17):2699. doi: 10.3390/cells11172699. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078112 Free PMC article.
-
Salinization Dramatically Enhance the Anti-Prostate Cancer Efficacies of AR/AR-V7 and Mnk1/2 Molecular Glue Degraders, Galeterone and VNPP433-3β Which Outperform Docetaxel and Enzalutamide in CRPC CWR22Rv1 Xenograft Mouse Model.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Oct;139:106700. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106700. Epub 2023 Jun 25. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37392559 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling reveals that VNPP433-3β, the lead next-generation galeterone analog inhibits prostate cancer stem cells by downregulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell markers.Mol Carcinog. 2022 Jul;61(7):643-654. doi: 10.1002/mc.23406. Epub 2022 May 5. Mol Carcinog. 2022. PMID: 35512605 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Androgen Receptor Splice Variant 7 in the Treatment of Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer with Next generation Androgen Receptor Signal Inhibition: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Eur Urol Focus. 2018 Jul;4(4):529-539. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Eur Urol Focus. 2018. PMID: 28753843
-
Androgen receptor targeting drugs in castration-resistant prostate cancer and mechanisms of resistance.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Dec;98(6):582-9. doi: 10.1002/cpt.256. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26331358 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Murine toxicology and pharmacokinetics of lead next generation galeterone analog, VNPP433-3β.Steroids. 2023 Apr;192:109184. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2023.109184. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Steroids. 2023. PMID: 36702363 Free PMC article.
-
Deeping in the Role of the MAP-Kinases Interacting Kinases (MNKs) in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 23;21(8):2967. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082967. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32340135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Next-Generation Androgen Receptor-Targeted Therapeutics in Development for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 20;22(4):2124. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042124. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33672769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel AR/AR-V7 and Mnk1/2 Degrader, VNPP433-3β: Molecular Mechanisms of Action and Efficacy in AR-Overexpressing Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo Models.Cells. 2022 Aug 30;11(17):2699. doi: 10.3390/cells11172699. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078112 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 1,2,5-Trisubstituted Benzimidazoles Potentiate Apoptosis by Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Panel of Cancer Cells.ACS Omega. 2022 Dec 6;7(50):46955-46971. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06057. eCollection 2022 Dec 20. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36570271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kwegyir-Afful A.K., Ramalingam S., Purushottamachar P., Ramamurthy V.P., Njar V.C. Galeterone and VNPT55 induce proteasomal degradation of AR/AR-V7, induce significant apoptosis via cytochrome c release and suppress growth of castration resistant prostate cancer xenografts in vivo. Oncotarget. 2015;6:27440–27460. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4578. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Purushottamachar P., Godbole A.M., Gediya L.K., Martin M.S., Vasaitis T.S., Kwegyir-Afful A.K., Ramalingam S., Ates-Alagoz Z., Njar V.C. Systematic structure modifications of multitarget prostate cancer drug candidate galeterone to produce novel androgen receptor down-regulating agents as an approach to treatment of advanced prostate cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2013;56:4880–4898. doi: 10.1021/jm400048v. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

