Insights on Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinases (CPKs) Signaling for Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants
- PMID: 31653073
- PMCID: PMC6862689
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20215298
Insights on Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinases (CPKs) Signaling for Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants
Abstract
Abiotic stresses are the major limiting factors influencing the growth and productivity of plants species. To combat these stresses, plants can modify numerous physiological, biochemical, and molecular processes through cellular and subcellular signaling pathways. Calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs or CPKs) are the unique and key calcium-binding proteins, which act as a sensor for the increase and decrease in the calcium (Ca) concentrations. These Ca flux signals are decrypted and interpreted into the phosphorylation events, which are crucial for signal transduction processes. Several functional and expression studies of different CPKs and their encoding genes validated their versatile role for abiotic stress tolerance in plants. CPKs are indispensable for modulating abiotic stress tolerance through activation and regulation of several genes, transcription factors, enzymes, and ion channels. CPKs have been involved in supporting plant adaptation under drought, salinity, and heat and cold stress environments. Diverse functions of plant CPKs have been reported against various abiotic stresses in numerous research studies. In this review, we have described the evaluated functions of plant CPKs against various abiotic stresses and their role in stress response signaling pathways.
Keywords: ABA; calcium signaling; calcium-dependent protein kinases; drought; salinity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
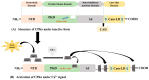
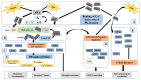
References
-
- Asano T., Hayashi N., Kobayashi M., Aoki N., Miyao A., Mitsuhara I., Ichikawa H., Komatsu S., Hirochika H., Kikuchi S. A rice calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCPK12 oppositely modulates salt-stress tolerance and blast disease resistance. Plant J. 2012;69:26–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04766.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang W., Zhang H., Wei X., Yang L., Yang B., Zhang L., Li J., Jiang Y.-Q. Functional characterization of calcium-dependent protein kinase (CPK) 2 gene from oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) in regulating reactive oxygen species signaling and cell death control. Gene. 2018;651:49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.02.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

