Development of In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation for Upadacitinib Extended-Release Tablet Formulation
- PMID: 31654328
- PMCID: PMC6814631
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-019-0378-y
Development of In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation for Upadacitinib Extended-Release Tablet Formulation
Abstract
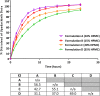
Upadacitinib is a selective Janus Kinase 1 inhibitor which is being developed for the treatment of several inflammatory diseases including rheumatoid arthritis. Upadacitinib was evaluated in Phase 3 studies as an oral extended-release (ER) formulation administered once daily. The purpose of this study was to develop a level A in vitro-in vivo correlation (IVIVC) for upadacitinib ER formulation. The pharmacokinetics of four upadacitinib extended-release formulations with different in vitro release characteristics and an immediate-release capsule formulation of upadacitinib were evaluated in 20 healthy subjects in a single-dose, randomized, crossover study. In vivo pharmacokinetic data and in vitro dissolution data (USP Dissolution Apparatus 1; pH 6.8; 100 rpm) were used to establish a level A IVIVC. Three formulations were used to establish the IVIVC, and the fourth formulation was used for external validation. A non-linear IVIVC best described the relationship between upadacitinib in vitro dissolution and in vivo absorption profiles. The absolute percent prediction errors (%PE) for upadacitinib Cmax and AUC were less than 10% for all three formulations used to establish the IVIVC, as well as for the %PE for the external validation formulation and the overall mean internal validation. Model was cross-validated using the leave-one-out approach; all evaluated cross-validation runs met the regulatory acceptance criteria. A level A IVIVC was successfully developed and validated for upadacitinib ER formulation, which meets the FDA and EMA regulatory validation criteria and can be used as surrogate for in vivo bioequivalence.
Keywords: ABT-494; extended-release formulation; in vitro/in vivo correlations (IVIVC); pharmacokinetics; upadacitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of AbbVie Inc. and may hold AbbVie stocks or options.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Upadacitinib Using the Immediate-Release and Extended-Release Formulations in Healthy Subjects and Subjects with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Analyses of Phase I-III Clinical Trials.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Aug;58(8):1045-1058. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00739-3. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 30945116 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics of Upadacitinib in Healthy Subjects and Subjects With Rheumatoid Arthritis, Crohn's Disease, Ulcerative Colitis, or Atopic Dermatitis: Population Analyses of Phase 1 and 2 Clinical Trials.J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;60(4):528-539. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1550. Epub 2019 Nov 7. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31701537
-
Development of a Level A in Vitro-in Vivo Correlation for Veliparib (ABT-888) Extended Release Tablet Formulation.Pharm Res. 2017 Jun;34(6):1187-1192. doi: 10.1007/s11095-017-2133-3. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28243955 Clinical Trial.
-
In vitro - In vivo correlation in the development of oral drug formulation: A screenshot of the last two decades.Int J Pharm. 2020 Apr 30;580:119210. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119210. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32173499 Review.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Upadacitinib in Healthy Subjects and Subjects with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Analyses of Phase I and II Clinical Trials.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018 Aug;57(8):977-988. doi: 10.1007/s40262-017-0605-6. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018. PMID: 29076110 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
α-Mangostin Nanoparticles Cytotoxicity and Cell Death Modalities in Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Molecules. 2021 Aug 24;26(17):5119. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175119. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing Extended-release Formulation of l-tetrahydropalmatine Based on In Vivo Outcomes Using Integrated Modeling Approaches.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 Jun 26;26(6):170. doi: 10.1208/s12249-025-03165-w. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 40562959
-
Model-Informed Paradigm in Drug Development-An End-To-End Case Study From Upadacitinib Development.Clin Transl Sci. 2025 Aug;18(8):e70295. doi: 10.1111/cts.70295. Clin Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40763919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world effectiveness of upadacitinib in Crohn's disease: a UK multicentre retrospective cohort study.Frontline Gastroenterol. 2024 Jul;15(4):297-304. doi: 10.1136/flgastro-2024-102668. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38903490 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Upadacitinib: Review of Data Relevant to the Rheumatoid Arthritis Indication.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020 May;59(5):531-544. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00855-0. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020. PMID: 31867699 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parmentier JM, Voss J, Graff C, Schwartz A, Argiriadi M, Friedman M, Camp HS, Padley RJ, George JS, Hyland D, Rosebraugh M, Wishart N, Olson L, Long AJ. In vitro and in vivo characterization of the JAK1 selectivity of upadacitinib (ABT-494) BMC Rheumatol. 2018;2(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s41927-018-0031-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burmester GR, Kremer JM, Van den Bosch F, Kivitz A, Bessette L, Li Y, et al. Safety and efficacy of upadacitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (SELECT-NEXT): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10139):2503–12. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31115-2. - PubMed
-
- Kremer JM, Emery P, Camp HS, Friedman A, Wang L, Othman AA, Khan N, Pangan AL, Jungerwirth S, Keystone EC. A phase IIb study of ABT-494, a selective JAK-1 inhibitor, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2016;68(12):2867–2877. doi: 10.1002/art.39801. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

