Partial ALPPS versus complete ALPPS for staged hepatectomy
- PMID: 31655548
- PMCID: PMC6815396
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-019-1090-1
Partial ALPPS versus complete ALPPS for staged hepatectomy
Abstract
Background: Associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy (ALPPS) can induce a stronger regenerative ability than traditional 2-stage hepatectomy (TSH). ALPPS has become popular for achieving fast hypertrophy in patients with an insufficient future liver remnant (FLR). However, ALPPS is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Partial ALPPS is a variation that may decrease the morbidity and mortality. The purpose of this study was to perform a meta-analysis comparing outcomes of ALLPS and partial ALLPS.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases were searched for studies comparing partial ALPPS and complete ALPPS up to April 2019. Included studies were assessed by the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS). Weighted mean difference (WMD)/standard mean difference (SMD) and odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to compare FLR, time interval between stages, postoperative complications, and mortality between partial and complete ALPPS.
Results: Four studies including 124 patients were included. FLR hypertrophy of partial ALPPS was comparable to complete ALPPS (p = 0.09). The time interval between stages was not different between the 2 procedures (p = 0.57). The postoperative complications rate of partial ALPPS was significantly lower than that of complete ALPPS (OR = 0.38; p = 0.03). The mortality rate of partial ALLPS (4.9%) was lower than that of complete ALLPS (18.9%), but the difference was not significant (OR = 0.37; p = 0.12).
Conclusions: Partial ALLPS is associated with similar FLR hypertrophy and time interval between stages as complete ALLPS, and a lower complication rate. Further studies are needed to examine patient selection and outcomes of the 2 procedures.
Keywords: Complete ALPPS; Future liver remnant; Hepatectomy; Partial ALPPS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


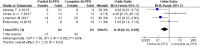
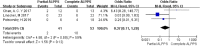
References
-
- Jaeck D, Oussoultzoglou E, Rosso E, Greget M, Weber JC, Bachellier P. A two-stage hepatectomy procedure combined with portal vein embolization to achieve curative resection for initially unresectable multiple and bilobar colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg. 2004;240:1037–1049. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000145965.86383.89. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schnitzbauer AA, Lang SA, Goessmann H, Nadalin S, Baumgart J, Farkas SA, et al. Right portal vein ligation combined with in situ splitting induces rapid left lateral liver lobe hypertrophy enabling 2-staged extended right hepatic resection in small-for-size settings. Ann Surg. 2012;255:405–414. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31824856f5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

