Renovascular Hypertension
- PMID: 31655775
- PMCID: PMC7184322
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ecl.2019.08.007
Renovascular Hypertension
Abstract
Renovascular disease (RVD) is a major cause of secondary hypertension. Atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis is the most common type of RVD followed by fibromuscular dysplasia. It has long been recognized as the prototype of angiotensin-dependent hypertension. However, the mechanisms underlying the physiopathology of hypertensive occlusive vascular renal disease are complex and distinction between the different causes of RVD should be made. Recognition of these distinct types of RVD with different degrees of renal occlusive disease is important for management. The greatest challenge is to individualize and implement the best approach for each patient in the setting of widely different comorbidities.
Keywords: Hypertension; Ischemic nephropathy; Renal artery stenosis; Renin and angiotensin; Renovascular disease.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

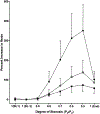

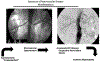

References
-
- Basso N, Terragno NA. History about the discovery of the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension (Dallas, Texas : 1979) 2001;38:1246–9. - PubMed
-
- Stanley JC. David M. Hume memorial lecture. Surgical treatment of renovascular hypertension. American Journal of Surgery 1997;174:102–10. - PubMed
-
- Drieghe B, Madaric J, Sarno G, et al. Assessment of renal artery stenosis: side-by-side comparison of angiography and duplex ultrasound with pressure gradient measurements. European Heart Journal 2008;29:517–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

