Efficacy of plasma rich in growth factor used for dry socket management: a systematic review
- PMID: 31655828
- PMCID: PMC6901146
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.23015
Efficacy of plasma rich in growth factor used for dry socket management: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: The main aim of this systematic review was to assess the dry socket management using plasma rich in growth factor (PRGF) in terms of pain relief, alveolar fossa healing, inflammation, the incidence of dry socket.
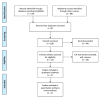
Material and methods: PubMed, Cochrane Library, Elsevier Science Direct, China Biology Medicine (CBM), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) and VIP database were searched for the related articles without language limitation. Two reviewers independently searched and evaluated relevant studies. This review has been registered in the website PROSPERO (CRD42018087252).
Results: 28 articles were retrieved on PubMed and 98 on other electronic databases in the initial search. In the end, 4 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included, with a total of 139 patients enrolled. The descriptive results indicated that the use of PRGF may help reduce pain and inflammation after tooth extraction. To some extent, it is beneficial to the management of dry socket after extraction.
Conclusions: Quality assessment indicated all the included studies were judged to be at high risk of bias with low quality. Hence, it was impossible to make a recommendation for clinical use of PRGF based on the current evidence. Clearly, a multicenter clinical randomized controlled trial is needed urgent to evaluate the safety and efficacy of PRGF for dry socket management.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exist.
Figures
References
-
- Bui CH, Seldin EB, Dodson TB. Types, frequencies, and risk factors for complications after third molar extraction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;61:1379–89. - PubMed
-
- Larsen PE. Alveolar osteitis after surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molars. Identification of the patient at risk. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1992;73:393–97. - PubMed
-
- Parthasarathi K, Smith A, Chandu A. Factors affecting incidence of dry socket: a prospective community-based study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;69:1880–84. - PubMed
-
- Blum IR. Contemporary views on dry socket (alveolar osteitis): a clinical appraisal of standardization, aetiopathogenesis and management: a critical review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;31:309–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources