Association of inflammatory biomarkers with lung cancer in North Indian population
- PMID: 31656499
- PMCID: PMC6794528
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v19i2.39
Association of inflammatory biomarkers with lung cancer in North Indian population
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is characterized by uncontrolled cell growth of the lung tissues. It is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
Objectives: The study aimed to determine the circulating CRP, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 levels in lung cancer and healthy control and also established association between these biomarkers with the smoking status as well as the stages of the disease.
Methodology: 51 lung cancer patients and 51 healthy controls were enrolled in this case-control study. The serum levels of CRP, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 were measured in lung cancer patients and healthy control groups.
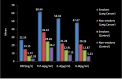
Results: The levels of serum CRP, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 were significantly higher in lung cancer patients when compared with controls(P<0.0001). The levels of these biomarkers were also significantly higher in stage iii/iv as compared to stage i/ii(P<0.001). Significant difference in the levels of these biomarkers were also found in smoker and non-smoker lung cancer patients as compared to controls(P<0.001).
Conclusion: CRP, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 are the promising biomarkers in the identification of lung cancer patients. The study also supports the association of inflammatory markers to lung cancer risk. Hence these findings suggest the levels of these biomarkers could be a useful tool for guiding the diagnosis of lung cancer.
Keywords: Lung cancer; biomarker; inflammation; smoking; stage.
© 2019 Gaur et al.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):9–29. - PubMed
-
- Mack CL. Serum cytokines as biomarkers of disease and clues to pathogenesis. Hepatology. 2007;46(1):6–8. - PubMed
-
- Seruga B, Zhang H, Bernstein LJ, Tannock IF. Cytokines and their relationship to the symptoms and outcome of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(11):887–899. - PubMed
-
- Smyth MJ, Cretney E, Kershaw MH, Hayakawa Y. Cytokines in cancer immunity and immunotherapy. Immunol Rev. 204;202(1):275–293. PubMed. - PubMed
-
- Chang CH, Hsiao CF, Yeh YM, Chang GC, Tsai YH, et al. Circulating interleukin-6 level is a prognostic marker for survival in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(9):1977–1985. PubMed. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
