Alkaline serine protease from the new halotolerant alkaliphilic Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens strain AK-R: purification and properties
- PMID: 31656729
- PMCID: PMC6787118
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-019-1928-9
Alkaline serine protease from the new halotolerant alkaliphilic Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens strain AK-R: purification and properties
Abstract
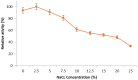
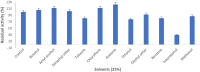
Herein, we report the purification and characterization of an alkaline protease from the alkaliphilic Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens (formerly Bacillus agaradhaerens) strain AK-R, which was previously isolated from Egyptian soda lakes. The purification procedures resulted in enzyme purification up to 13.3-fold, with a recovery yield of 16.3% and a specific activity of 3488 U/mg protein. AK-R protease was a monomeric protein with an estimated molecular weight of 33.0 kDa. The optimum pH and temperature for AK-R protease were pH 10 and 60 °C, respectively. The enzyme thermostability was significantly enhanced in the presence of CaCl2 by approximately 1.3-fold. Moreover, under optimal conditions, the K m and V max values of the enzyme were 2.63 mg/ml and 4166.7 U/mg, respectively. PMSF caused complete inhibition of the enzyme activity, suggesting that AK-R belongs to the serine protease family. In addition, the enzyme was completely inhibited by EDTA, revealing the requirement of metal ions for AK-R protease activity; hence, it can be classified as a metalloprotease. AK-R protease is a mostly thiol-independent enzyme, since thiol reductants such as β-mercaptoethanol and dithiothreitol had no effect on the enzyme activity. AK-R protease exhibited high stability in several organic solvents, including butanol, amyl alcohol, dimethyl ether, toluene, diethyl ether and methanol. Moreover, AK-R protease showed significant stability to a variety of surfactants and commercial detergents. The features and properties of AK-R alkaline protease are favourable and suggest its potential applications in various industries, particularly in the laundry detergent industry.
Keywords: Alkaline proteases; Alkaliphilic bacteria; Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens; Soda lakes.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThere is no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Abidi F, Chobert JM, Haertlé T, Marzouki MN. Purification and biochemical characterization of stable alkaline protease Prot-2 from Botrytis cinerea. Process Biochem. 2011;46(12):2301–2310.
-
- Al-Salamah AA, El-Badawi YB, El-Tayeb MA, Antranikian G. Detergent-, solvent- and salt-compatible thermoactive alkaline serine protease from halotolerant alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. NPST-AK15: purification and characterization. Extremophiles. 2015;19(5):961–971. - PubMed
-
- Annamalai N, Rajeswari MV, Balasubramanian T. Extraction, purification and application of thermostable and halostable alkaline protease from Bacillus alveayuensis CAS 5 using marine wastes. Food Bioprod Process. 2014;92(4):335–342.
-
- Asker MM, Mahmoud MG, El-Shebwy K, El Aziz MA. Purification and characterization of two thermostable protease fractions from Bacillus megaterium. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2013;11:103–109.
-
- Banerjee G, Mukherjee S, Bhattacharya S, Arun K, Ray AR. Purification and characterization of extracellular protease and amylase produced by the bacterial strain, Corynebacterium alkanolyticum ATH3 isolated from fish gut, Arab. J Sci Eng. 2016;41:9–16.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

