Expanding congenital abnormalities of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT) genetics: basonuclin 2 (BNC2) and lower urinary tract obstruction
- PMID: 31656805
- PMCID: PMC6789316
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2019.08.73
Expanding congenital abnormalities of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT) genetics: basonuclin 2 (BNC2) and lower urinary tract obstruction
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
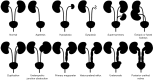
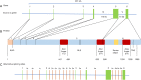
Comment in
-
Expanding the knowledge on development of CAKUT: molecular genetics and beyond.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Oct;7(20):596. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.157. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31807577 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Rare Variants in BNC2 Are Implicated in Autosomal-Dominant Congenital Lower Urinary-Tract Obstruction.Am J Hum Genet. 2019 May 2;104(5):994-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.03.023. Am J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31051115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ortiz A, Sanchez-Niño MD, Crespo-Barrio M, et al. The Spanish Society of Nephrology (SENEFRO) commentary to the Spain GBD 2016 report: Keeping chronic kidney disease out of sight of health authorities will only magnify the problem. Nefrologia 2019;39:29-34. 10.1016/j.nefro.2018.09.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Foreman KJ, Marquez N, Dolgert A, et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: reference and alternative scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018;392:2052-90. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31694-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
