Glycyrrhizin mitigates radiation-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4 signalling pathway
- PMID: 31657123
- PMCID: PMC6933400
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14703
Glycyrrhizin mitigates radiation-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4 signalling pathway
Abstract
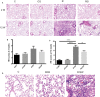
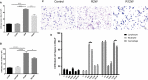
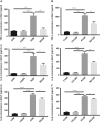
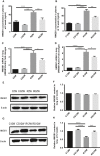
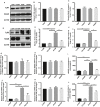
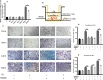
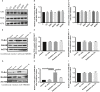
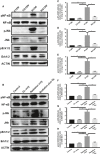
Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is the major complication of thoracic radiation therapy, and no effective treatment is available. This study explored the role of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in acute RILI and the therapeutic effect of glycyrrhizin, an inhibitor of HMGB1, on RILI. C57BL/6 mice received a 20 Gy dose of X-ray radiation to the whole thorax with or without administration of glycyrrhizin. Severe lung inflammation was present 12 weeks after irradiation, although only a mild change was noted at 2 weeks and could be alleviated by administration of glycyrrhizin. Glycyrrhizin decreased the plasma concentrations of HMGB1 and sRAGE as well as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 levels in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). The expression of RAGE was decreased while that of TLR4 was significantly increased at 12 weeks, but not 2 weeks, after irradiation in mouse lung tissue. In vitro, the expression of TLR4 increased in RAW 264.7 cells after conditioning with the supernatant from the irradiated MLE-12 cells containing HMGB1 but showed no change when conditioned medium without HMGB1 was used. However, conditioned culture had no effect on RAGE expression in RAW 264.7 cells. Glycyrrhizin also inhibited the related downstream transcription factors of HMGB/TLR4, such as NF-κB, JNK and ERK1/2, in lung tissue and RAW 264.7 cells when TLR4 was activated. In conclusion, the HMGB1/TLR4 pathway mediates RILI and can be mitigated by glycyrrhizin.
Keywords: HMGB1; RAGE; TLR4; glycyrrhizin; radiation-induced lung injury (RILI).
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Simone CB 2nd. Thoracic radiation normal tissue injury. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2017;27:370‐377. - PubMed
-
- Rube CE, Uthe D, Schmid KW, et al. Dose‐dependent induction of transforming growth factor beta (TGF‐beta) in the lung tissue of fibrosis‐prone mice after thoracic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;47:1033‐1042. - PubMed
-
- Minami‐Shimmyo Y, Ohe Y, Yamamoto S, et al. Risk factors for treatment‐related death associated with chemotherapy and thoracic radiotherapy for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7:177‐182. - PubMed
-
- Hekim N, Cetin Z, Nikitaki Z, et al. Radiation triggering immune response and inflammation. Cancer Lett. 2015;368:156‐163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

