Ift88 is involved in mandibular development
- PMID: 31657471
- PMCID: PMC6956436
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.13096
Ift88 is involved in mandibular development
Abstract
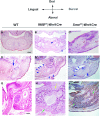
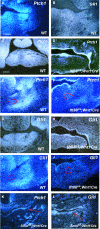
The mandible is a crucial organ in both clinical and biological fields due to the high frequency of congenital anomalies and the significant morphological changes during evolution. Primary cilia play a critical role in many biological processes, including the determination of left/right axis patterning, the regulation of signaling pathways, and the formation of bone and cartilage. Perturbations in the function of primary cilia are known to cause a wide spectrum of human diseases: the ciliopathies. Craniofacial dysmorphologies, including mandibular deformity, are often seen in patients with ciliopathies. Mandibular development is characterized by chondrogenesis and osteogenesis; however, the role of primary cilia in mandibular development is not fully understood. To address this question, we generated mice with mesenchymal deletions of the ciliary protein, Ift88 (Ift88fl/fl ;Wnt1Cre). Ift88fl/fl ;Wnt1Cre mice showed ectopic mandibular bone formation, whereas Ift88 mutant mandible was slightly shortened. Meckel's cartilage was modestly expanded in Ift88fl/fl ;Wnt1Cre mice. The downregulation of Hh signaling was found in most of the mesenchyme of Ift88 mutant mandible. However, mice with a mesenchymal deletion of an essential molecule for Hh signaling activity, Smo (Smofl/fl ;Wnt1Cre), showed only ectopic mandibular formation, whereas Smo mutant mandible was significantly shortened. Ift88 is thus involved in chondrogenesis and osteogenesis during mandibular development, partially through regulating Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling.
Keywords: Hedgehog signaling; Ift88; Meckel's cartilage; mandibular bone.
© 2019 Anatomical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Adel Al‐Lami H, Barrell WB, Liu KJ (2016) Micrognathia in mouse models of ciliopathies. Biochem Soc Trans 44, 1753–1759. - PubMed
-
- Billmyre KK, Klingensmith J (2015) Sonic hedgehog from pharyngeal arch 1 epithelium is necessary for early mandibular arch cell survival and later cartilage condensation differentiation. Dev Dyn 244, 564–576. - PubMed
-
- Bimonte S, De Angelis A, Quagliata L, et al. (2011) Ofd1 is required in limb bud patterning and endochondral bone development. Dev Biol 349, 179–191. - PubMed
-
- Bisgrove BW, Yost HJ (2006) The roles of cilia in developmental disorders and disease. Development 133, 4131–4143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

