Diagnostic kit for rice blight resistance
- PMID: 31659338
- PMCID: PMC6831515
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-019-0268-y
Diagnostic kit for rice blight resistance
Abstract
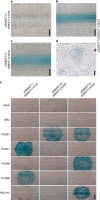
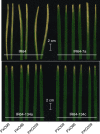
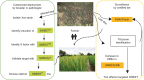
Blight-resistant rice lines are the most effective solution for bacterial blight, caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). Key resistance mechanisms involve SWEET genes as susceptibility factors. Bacterial transcription activator-like (TAL) effectors bind to effector-binding elements (EBEs) in SWEET gene promoters and induce SWEET genes. EBE variants that cannot be recognized by TAL effectors abrogate induction, causing resistance. Here we describe a diagnostic kit to enable analysis of bacterial blight in the field and identification of suitable resistant lines. Specifically, we include a SWEET promoter database, RT-PCR primers for detecting SWEET induction, engineered reporter rice lines to visualize SWEET protein accumulation and knock-out rice lines to identify virulence mechanisms in bacterial isolates. We also developed CRISPR-Cas9 genome-edited Kitaake rice to evaluate the efficacy of EBE mutations in resistance, software to predict the optimal resistance gene set for a specific geographic region, and two resistant 'mega' rice lines that will empower farmers to plant lines that are most likely to resist rice blight.
Conflict of interest statement
W.B.F., J.S.E., F.W., B.Y. and R.O. are inventors on US provisional patent application 62832300 that covers Kitaake, IR64 and Ciherang-Sub1 EBE-edited lines and kit components described here.
Figures

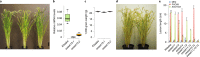

References
-
- Mew TW. Current status and future prospects of research on bacterial blight of rice. Annu. Rev. Phytopath. 1987;25:359–382.
-
- Ke Y, Deng H, Wang S. Advances in understanding broad-spectrum resistance to pathogens in rice. Plant J. 2017;90:738–748. - PubMed
-
- Government of India. State of Indian Agriculture 2015–16 (Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Cooperation & Farmers Welfare Directorate of Economics & Statistics Department of Agriculture, 2016).
-
- Laha, G. S. et al. Changes in Rice Disease Scenario in India: An Analysis from Production Oriented Survey (ICAR–Indian Institute of Rice Research, 2016).
-
- Duku C, Sparks AH, Zwart SJ. Spatial modelling of rice yield losses in Tanzania due to bacterial leaf blight and leaf blast in a changing climate. Clim. Change. 2016;135:569–583.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

