Cystic trigeminal schwannomas
- PMID: 31660099
- PMCID: PMC6807068
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2019.09.031
Cystic trigeminal schwannomas
Abstract
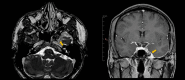
Trigeminal Schwannomas are less than 1% of intracranial tumors, of which only 7% have a cystic component. We documented 2 cases of males with cystic trigeminal Schwannomas, their symptoms, the diagnosis process and the imaging characteristics. In addition, a review of the literature is performed, with emphasis on the radiological classification of this rare entity, that constitutes a diagnostic challenge for the radiologist, who has an essential role in the approach to the disease and therefore in its management.
Keywords: Magnetic resonance imaging; Trigeminal cystic schwannoma.
© 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures


References
-
- Gennaro P., Nastro Siniscalchi E., Gabriele G., Cascone P., Siniscalchi E.N., Gabriele G. Trigeminal and facial schwannoma : a case load and review of the literature. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci [Internet] 2012;16:8–12. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23090796 [cited 2015 Oct 2]Available from: - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A. Intracranial trigeminal schwannoma. Neuroradiol J. 2014;27(Trevo 2):0. http://neu.sagepub.com/lookup/doi/10.15274/NRJ-2014-10117 [Internet][cited 2015 Oct 2]Available from: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Acharya V., Williams a., Adams W., Hilton D., Whitfield P.C. Middle cranial fossa cystic schwannoma. Case Rep [Internet] 2012;2012 http://casereports.bmj.com/cgi/doi/10.1136/bcr.12.2011.5356 bcr1220115356-bcr1220115356. Available from: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wanibuchi M., Fukushima T., Zomordi A.R., Nonaka Y., Friedman A.H. Trigeminal schwannomas. Neurosurgery [Internet] 2012;70:ons132–ons144. http://content.wkhealth.com/linkback/openurl?sid=WKPTLP:landingpage&an=0... Available from: - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen J, Lindekaer A, Ostergaard H, Mehra S, Garga UC. Case report radiological imaging in trigeminal nerve schwannoma : a case report and review of literature. 2013;26(2):117–119.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

