Nanoemulsified adlay bran oil reduces tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in B16F10 cells and zebrafish
- PMID: 31660135
- PMCID: PMC6804758
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.1176
Nanoemulsified adlay bran oil reduces tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in B16F10 cells and zebrafish
Abstract
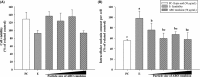
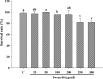
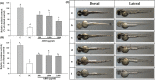
The efficacy of oily components is often difficult to evaluate due to their incompatibility with most models. Here, we emulsified adlay bran oil (ABO), processed it to a nanoscale, and investigated its anti-hyperpigmentation efficacy, assessed for its inhibitory effects against tyrosinase activity and melanin production, in an in vitro system (mouse melanoma B16F10 cells) and an in vivo system (zebrafish embryos). ABO induced dose-dependent reductions in tyrosinase activity and melanin production in both the melanoma cells and zebrafish, without affecting viability. The efficacy of ABO was strongly influenced by emulsion particle size in the zebrafish but not in the cells. These results indicate that ABO has potential as a tyrosinase inhibitor and anti-hyperpigmentation agent and that the emulsion system is an effective method for delivering the bioactive components of ABO to living systems that could be utilized for other oily components.
Keywords: adlay bran oil; anti‐hyperpigmentation; melanin; nanoemulsion; tyrosinase; zebrafish.
© 2019 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Attenuation of in vitro and in vivo melanin synthesis using a Chinese herbal medicine through the inhibition of tyrosinase activity.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jan;95:153876. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153876. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 34923233
-
Inhibitory effects of adlay extract on melanin production and cellular oxygen stress in B16F10 melanoma cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Sep 19;15(9):16665-79. doi: 10.3390/ijms150916665. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25244016 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Amide Derivatives as Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitors; In-vitro, In-vivo Antimelanogenic Activity and Computational Studies.Med Chem. 2019;15(7):715-728. doi: 10.2174/1573406415666190319101329. Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30892163
-
Assessment of Cuscuta chinensis seeds׳ effect on melanogenesis: comparison of water and ethanol fractions in vitro and in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 May 28;154(1):240-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.04.016. Epub 2014 Apr 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24746484
-
Inhibitory Effects of Caulerpa racemosa, Ulva intestinalis, and Lobophora challengeriae on Tyrosinase Activity and α-MSH-Induced Melanogenesis in B16F10 Melanoma Cells.Life (Basel). 2023 Apr 3;13(4):934. doi: 10.3390/life13040934. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37109464 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dual Antimelanogenic Effect of Nicotinamide-Stabilized Phloretin Nanocrystals in Larval Zebrafish.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 30;14(9):1825. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091825. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145574 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection and Enhanced Learning and Memory Abilities of Steamed American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolium L.) Based on Zebrafish.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jun 1;13(6):e70369. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70369. eCollection 2025 Jun. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40458084 Free PMC article.
-
Energy-Based Methods and Nanocarrier-Based Approaches for Melasma Treatment.Adv Pharm Bull. 2024 Dec 30;14(4):759-793. doi: 10.34172/apb.42794. Epub 2024 Sep 15. Adv Pharm Bull. 2024. PMID: 40190686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Metabolism and its Mechanism Triggered by Supercritical CO2 Extract of Adlay (Coix lacryma-jobi var. ma-yuen (Rom. Caill.) Stapf) Bran in High-Fat Diet Induced Hyperlipidemic Hamsters.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 17;12:785944. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.785944. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867418 Free PMC article.
-
Actional Mechanisms of Active Ingredients in Functional Food Adlay for Human Health.Molecules. 2022 Jul 27;27(15):4808. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154808. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956759 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bodmeier, R. , Chen, H. , & Paeratakul, O. (1989). A novel approach to the oral delivery of micro‐or nanoparticles. Pharmaceutical Research, 6, 413–417. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

