Unfold: an integrated toolbox for overlap correction, non-linear modeling, and regression-based EEG analysis
- PMID: 31660265
- PMCID: PMC6815663
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.7838
Unfold: an integrated toolbox for overlap correction, non-linear modeling, and regression-based EEG analysis
Abstract
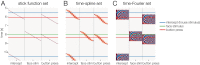
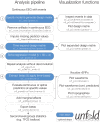
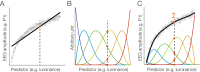
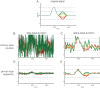
Electrophysiological research with event-related brain potentials (ERPs) is increasingly moving from simple, strictly orthogonal stimulation paradigms towards more complex, quasi-experimental designs and naturalistic situations that involve fast, multisensory stimulation and complex motor behavior. As a result, electrophysiological responses from subsequent events often overlap with each other. In addition, the recorded neural activity is typically modulated by numerous covariates, which influence the measured responses in a linear or non-linear fashion. Examples of paradigms where systematic temporal overlap variations and low-level confounds between conditions cannot be avoided include combined electroencephalogram (EEG)/eye-tracking experiments during natural vision, fast multisensory stimulation experiments, and mobile brain/body imaging studies. However, even "traditional," highly controlled ERP datasets often contain a hidden mix of overlapping activity (e.g., from stimulus onsets, involuntary microsaccades, or button presses) and it is helpful or even necessary to disentangle these components for a correct interpretation of the results. In this paper, we introduce unfold, a powerful, yet easy-to-use MATLAB toolbox for regression-based EEG analyses that combines existing concepts of massive univariate modeling ("regression-ERPs"), linear deconvolution modeling, and non-linear modeling with the generalized additive model into one coherent and flexible analysis framework. The toolbox is modular, compatible with EEGLAB and can handle even large datasets efficiently. It also includes advanced options for regularization and the use of temporal basis functions (e.g., Fourier sets). We illustrate the advantages of this approach for simulated data as well as data from a standard face recognition experiment. In addition to traditional and non-conventional EEG/ERP designs, unfold can also be applied to other overlapping physiological signals, such as pupillary or electrodermal responses. It is available as open-source software at http://www.unfoldtoolbox.org.
Keywords: EEG; ERP; Generalized additive model; Linear modeling of EEG; Non-linear modeling; Open source toolbox; Overlap correction; Regression splines; Regression-ERP; Regularization.
© 2019 Ehinger and Dimigen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





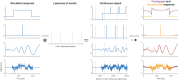
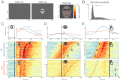
Similar articles
-
Regression-based analysis of combined EEG and eye-tracking data: Theory and applications.J Vis. 2021 Jan 4;21(1):3. doi: 10.1167/jov.21.1.3. J Vis. 2021. PMID: 33410892 Free PMC article.
-
The Decision Decoding ToolBOX (DDTBOX) - A Multivariate Pattern Analysis Toolbox for Event-Related Potentials.Neuroinformatics. 2019 Jan;17(1):27-42. doi: 10.1007/s12021-018-9375-z. Neuroinformatics. 2019. PMID: 29721680 Free PMC article.
-
Recording human electrocorticographic (ECoG) signals for neuroscientific research and real-time functional cortical mapping.J Vis Exp. 2012 Jun 26;(64):3993. doi: 10.3791/3993. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22782131 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond conventional event-related brain potential (ERP): exploring the time-course of visual emotion processing using topographic and principal component analyses.Brain Topogr. 2008 Jun;20(4):265-77. doi: 10.1007/s10548-008-0053-6. Epub 2008 Mar 13. Brain Topogr. 2008. PMID: 18338243 Review.
-
Linear Modeling of Neurophysiological Responses to Speech and Other Continuous Stimuli: Methodological Considerations for Applied Research.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 22;15:705621. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.705621. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34880719 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
fitgrid: A Python package for multi-channel event-related time series regression modeling.J Open Source Softw. 2021;6(63):3293. doi: 10.21105/joss.03293. Epub 2021 Jul 19. J Open Source Softw. 2021. PMID: 36310543 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Responses to Emotional Faces in Natural Settings: A Wireless Mobile EEG Recording Study.Front Psychol. 2018 Oct 25;9:2003. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02003. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30410458 Free PMC article.
-
Nonadditive integration of visual information in ensemble processing.iScience. 2023 Sep 19;26(10):107988. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107988. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37822498 Free PMC article.
-
Neural markers of error processing relate to task performance, but not to substance-related risks and problems and externalizing problems in adolescence and emerging adulthood.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2025 Jan;71:101500. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2024.101500. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39729859 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of mobile brain/body imaging studies using the P300 event-related potentials to investigate cognition beyond the laboratory.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2024 Aug;24(4):631-659. doi: 10.3758/s13415-024-01190-z. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38834886
References
-
- Baayen HR, Davidson DJ, Bates DM. Mixed-effects modeling with crossed random effects for subjects and items. Journal of Memory and Language. 2007;59(4):390–412. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2007.12.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

