Rescue of Replication-Competent ZIKV Hidden in Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Cells Long After the Resolution of the Infection
- PMID: 31660333
- PMCID: PMC6785694
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofz342
Rescue of Replication-Competent ZIKV Hidden in Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Cells Long After the Resolution of the Infection
Abstract
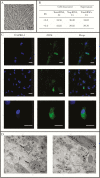
The Zika virus (ZIKV) genome, its negative-strand viral proteins, and virus-like particles were detected in placenta-derived mesenchymal cells (MSCs), indicating that ZIKV persists after virus clearance from maternal blood and can be rescued by in vitro cultivation. We report for the first time the presence of replication-competent ZIKV in MSCs from an asymptomatic woman who acquired infection during pregnancy.
Keywords: Zika virus; mesenchymal cells; placenta; vertical transmission; viral reservoir.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Wikan N, Smith DR. Zika virus: history of a newly emerging arbovirus. Lancet Infect Dis 2016; 16:e119–26. - PubMed
-
- Ministério da Saúde. Boletins epidemiológicos—Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde Available at: http://portalarquivos2.saude.gov.br/images/pdf/2018/janeiro/10/2017-046-.... Accessed 2 November 2018.
-
- de Araújo TVB, Ximenes RAA, Miranda-Filho DB, et al. ; investigators from the Microcephaly Epidemic Research Group; Brazilian Ministry of Health; Pan American Health Organization; Instituto de Medicina Integral Professor Fernando Figueira; State Health Department of Pernambuco Association between microcephaly, Zika virus infection, and other risk factors in Brazil: final report of a case-control study. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18:328–36. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martines RB, Bhatnagar J, de Oliveira Ramos AM, et al. . Pathology of congenital Zika syndrome in Brazil: a case series. Lancet 2016; 388:898–904. - PubMed
-
- Schaub B, Monthieux A, Najihoullah F, et al. . Late miscarriage: another Zika concern? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2016; 207:240–1. - PubMed

