Albumin losses during hemodiafiltration: all dialyzers are not created equal - a case report
- PMID: 31660886
- PMCID: PMC6819538
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-019-1567-8
Albumin losses during hemodiafiltration: all dialyzers are not created equal - a case report
Abstract
Background: Online hemodiafiltration (OL-HDF) is associated with better removal of both small and middle molecules and might improve survival compared to conventional hemodialysis (HD). Nevertheless, hemodiafiltration (HDF) can lead to an increase in albumin loss across the dialyzer, especially with high permeability membrane and high convective volume (CV). We present the case of a patient treated by OL-HDF who developed severe hypoalbuminemia resulting from massive albumin loss into dialysate.
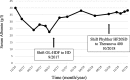
Case presentation: A 71-year-old woman with ESRD started renal replacement therapy in December 2016. She was treated by high volume post-dilution OL-HDF, 4 h, 3 times per week. The dialyzer was the Phylther HF20SD (a 2.0m2 heat sterilized high flux (HF) polyphenylene membrane from Bellco). At the initiation of dialysis, the serum albumin was 4.0 g/dl. During the following months, the patient developed severe hypoalbuminemia. The lowest value observed was 2.26 g/dl in July 2017. Diagnostic workup excluded nephrotic syndrome, hepatic failure and malabsorption. The patient was shifted from OL-HDF to standard HF HD, keeping the same dialyzer and dialysis schedule. During the following months, we observed a progressive correction of the hypoalbuminemia (3.82 g/dl at last follow-up). To precise the impact of the epuration technique on the albumin losses in this patient, we measured the amount of albumin in dialysate during one session with the Phylther HF20SD on OL-HDF and one session with the same filter but on standard HD. The CV was 29.0 l for the HDF session. The total albumin losses were 23.6 g on OL-HDF and 4.6 g on HD.
Conclusion: OL-HDF can lead to significant albumin loss into the dialysate, especially with high permeability membrane and high CV. When prescribing post-dilutional OL-HDF, the choice of the dialyzer membrane should be made with caution. Users of the steam sterilized polyphenylene membrane, the Phylther SD, should be informed of the risk of large albumin loss with this membrane during post-dilution OL-HDF.
Keywords: Albumin loss; Convective volume; High permeability membrane; Hypoalbuminemia; Online hemodiafiltration; Phylther SD; Polyphenylene membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous