The Effects of Rare SERPINA1 Variants on Lung Function and Emphysema in SPIROMICS
- PMID: 31661293
- PMCID: PMC7047460
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201904-0769OC
The Effects of Rare SERPINA1 Variants on Lung Function and Emphysema in SPIROMICS
Abstract
Rationale: The role of PI (protease inhibitor) type Z heterozygotes and additional rare variant genotypes in the gene encoding alpha-1 antitrypsin, SERPINA1 (serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A, member 1), in determining chronic obstructive pulmonary disease risk and severity is controversial.Objectives: To comprehensively evaluate the effects of rare SERPINA1 variants on lung function and emphysema phenotypes in subjects with significant tobacco smoke exposure using deep gene resequencing and alpha-1 antitrypsin concentrations.Methods: DNA samples from 1,693 non-Hispanic white individuals, 385 African Americans, and 90 Hispanics with ≥20 pack-years smoking were resequenced for the identification of rare variants (allele frequency < 0.05) in 16.9 kB of SERPINA1.Measurements and Main Results: White PI Z heterozygotes confirmed by sequencing (MZ; n = 74) had lower post-bronchodilator FEV1 (P = 0.007), FEV1/FVC (P = 0.003), and greater computed tomography-based emphysema (P = 0.02) compared with 1,411 white individuals without PI Z, S, or additional rare variants denoted as VR. PI Z-containing compound heterozygotes (ZS/ZVR; n = 7) had lower FEV1/FVC (P = 0.02) and forced expiratory flow, midexpiratory phase (P = 0.009). Nineteen white heterozygotes for five non-S/Z coding variants associated with lower alpha-1 antitrypsin had greater computed tomography-based emphysema compared with those without rare variants. In African Americans, a 5' untranslated region insertion (rs568223361) was associated with lower alpha-1 antitrypsin and functional small airway disease (P = 0.007).Conclusions: In this integrative deep sequencing study of SERPINA1 with alpha-1 antitrypsin concentrations in a heavy smoker and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease cohort, we confirmed the effects of PI Z heterozygote and compound heterozygote genotypes. We demonstrate the cumulative effects of multiple SERPINA1 variants on alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, lung function, and emphysema, thus significantly increasing the frequency of SERPINA1 variation associated with respiratory disease in at-risk smokers.
Keywords: SERPINA1; alpha-1 antitrypsin; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; emphysema; rare variant.
Figures
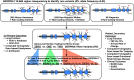

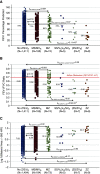

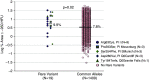
Comment in
-
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Mutations: Is One Too Many?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Mar 1;201(5):505-506. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201911-2209ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 31810377 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zaimidou S, van Baal S, Smith TD, Mitropoulos K, Ljujic M, Radojkovic D, et al. A1ATVar: a relational database of human SERPINA1 gene variants leading to alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency and application of the VariVis software. Hum Mutat . 2009;30:308–313. - PubMed
-
- Silverman EK, Sandhaus RA. Clinical practice: alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency. N Engl J Med . 2009;360:2749–2757. - PubMed
-
- Stoller JK, Aboussouan LS. Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency. Lancet . 2005;365:2225–2236. - PubMed
-
- Brantly M, Nukiwa T, Crystal RG. Molecular basis of alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Med . 1988;84:13–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100037C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900019C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HL141762/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018526/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL118128/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111527/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL137013/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900015C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900016C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL137880/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142992/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900013C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM101237/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900014C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900018C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK054759/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900017C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900020C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

