Sample preparation strategies for high-throughput mass spectrometry imaging of primary tumor organoids
- PMID: 31661714
- PMCID: PMC7254934
- DOI: 10.1002/jms.4452
Sample preparation strategies for high-throughput mass spectrometry imaging of primary tumor organoids
Abstract
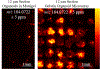
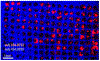
Patient-derived 3D organoids show great promise for understanding patient heterogeneity and chemotherapy response in human-derived tissue. The combination of organoid culture techniques with mass spectrometry imaging provides a label-free methodology for characterizing drug penetration, patient-specific response, and drug biotransformation. However, current methods used to grow tumor organoids employ extracellular matrices that can produce small molecule background signal during mass spectrometry imaging analysis. Here, we develop a method to isolate 3D human tumor organoids out of a Matrigel extracellular matrix into gelatin mass spectrometry compatible microarrays for high-throughput mass spectrometry imaging analysis. The alignment of multiple organoids in the same z-axis is essential for sectioning organoids together and for maintaining reproducible sample preparation on a single glass slide for up to hundreds of organoids. This method successfully removes organoids from extracellular matrix interference and provides an organized array for high-throughput imaging analysis to easily identify organoids by eye for area selection and further analysis. With this method, mass spectrometry imaging can be readily applied to organoid systems for preclinical drug development and personalized medicine research initiatives.
Keywords: MALDI MSI; drug discovery; high throughput; microwells; organoids.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

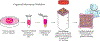

References
-
- Clinton J; McWilliams-Koeppen P, Initiation, Expansion, and Cryopreservation of Human Primary Tissue-Derived Normal and Diseased Organoids in Embedded Three-Dimensional Culture. Curr Protoc Cell Biol 2019, 82 (1), e66. - PubMed
-
- Drost J; Clevers H, Organoids in cancer research. Nature Reviews Cancer 2018, 18 (7), 407–418. - PubMed
-
- Romero-Calvo I; Weber CR; Ray M; Brown M; Kirby K; Nandi RK; Long TM; Sparrow SM; Ugolkov A; Qiang W; Zhang Y; Brunetti T; Kindler H; Segal JP; Rzhetsky A; Mazar AP; Buschmann MM; Weichselbaum R; Roggin K; White KP, Human Organoids Share Structural and Genetic Features with Primary Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Tumors. Mol Cancer Res 2019, 17 (1), 70–83. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beshiri ML; Tice CM; Tran C; Nguyen HM; Sowalsky AG; Agarwal S; Jansson KH; Yang Q; McGowen KM; Yin J; Alilin AN; Karzai FH; Dahut WL; Corey E; Kelly K, A PDX/Organoid Biobank of Advanced Prostate Cancers Captures Genomic and Phenotypic Heterogeneity for Disease Modeling and Therapeutic Screening. Clin Cancer Res 2018, 24 (17), 4332–4345. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

