Phosphorylation of RAB7 by TBK1/IKKε Regulates Innate Immune Signaling in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 31662325
- PMCID: PMC6942622
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1310
Phosphorylation of RAB7 by TBK1/IKKε Regulates Innate Immune Signaling in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
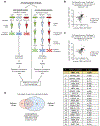
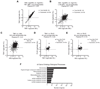
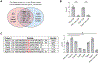
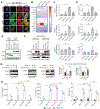
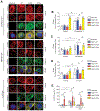
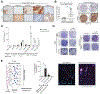
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a heterogeneous disease enriched for mutations in PTEN and dysregulation of innate immune signaling. Here, we demonstrate that Rab7, a recently identified substrate of PTEN phosphatase activity, is also a substrate of the innate immune signaling kinases TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1)/IκB kinase ε (IKKε) on the same serine-72 (S72) site. An unbiased search for novel TBK1/IKKε substrates using stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture phosphoproteomic analysis identified Rab7-S72 as a top hit. PTEN-null TNBC cells expressing a phosphomimetic version of Rab7-S72 exhibited diffuse cytosolic Rab7 localization and enhanced innate immune signaling, in contrast to a kinase-resistant version, which localized to active puncta that promote lysosomal-mediated stimulator of interferon genes (STING) degradation. Thus, convergence of PTEN loss and TBK1/IKKε activation on Rab7-S72 phosphorylation limited STING turnover and increased downstream production of IRF3 targets including CXCL10, CCL5, and IFNβ. Consistent with this data, PTEN-null TNBC tumors expressed higher levels of STING, and PTEN-null TNBC cell lines were hyperresponsive to STING agonists. Together, these findings begin to uncover how innate immune signaling is dysregulated downstream of TBK1/IKKε in a subset of TNBCs and reveals previously unrecognized cross-talk with STING recycling that may have implications for STING agonism in the clinic. SIGNIFICANCE: These findings identify Rab7 as a substrate for TBK1 for regulation of innate immune signaling, thereby providing important insight for strategies aimed at manipulating the immune response to enhance therapeutic efficacy in TNBC.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement. T.U.B. is a consultant for N-of-One/Qiagen. D.A.B. is consultant for N-of-One/Qiagen, Tango Therapeutics, and MADALON consulting. D.A.B. is cofounder of Xsphera Biosciences. D.A.B has received research funding from Novartis and Bristol Myers Squibb.
Figures
References
-
- Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L, Moore DT, Collichio F, et al. The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:2329–34 - PubMed
-
- Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andre F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:1275–81 - PubMed
-
- Phuah SY, Looi LM, Hassan N, Rhodes A, Dean S, Taib NA, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer and PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue) loss are predictors of BRCA1 germline mutations in women with early-onset and familial breast cancer, but not in women with isolated late-onset breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 2012;14:R142. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

