Developmental Aspects of Unintentional Injury Prevention Among Youth: Implications for Practice
- PMID: 31662723
- PMCID: PMC6796232
- DOI: 10.1177/1559827617745057
Developmental Aspects of Unintentional Injury Prevention Among Youth: Implications for Practice
Abstract
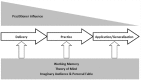
Unintentional injuries, the leading cause of morbidity and mortality among youth in the United States, are burdensome and costly to society. Continued prevention efforts to reduce rates of unintentional injury remain imperative. We emphasized the role of practitioner influence across a linear concept of injury prevention comprising delivery, practice, and application/generalization and within the context of child developmental factors. Specific strategies for injury prevention tailored to the cognitive development stage of the patient are provided. This information may be useful to health care practitioners, who have significant interaction with youth and their families.
Keywords: pediatrics; prevention; safety.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Injury prevention and control: welcome to WISQARSTM. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/wisqars/index.html. Accessed November 15, 2017.
-
- Alonge O, Hyder AA. Reducing the global burden of childhood unintentional injuries. Arch Dis Child. 2014;99:62-69. - PubMed
-
- Warnakulasuriya S. Effectiveness of tobacco counseling in the dental office. J Dent Educ. 2002;66:1079-1087. - PubMed
-
- Reinhartz J, Van Cleaf D. Teach-Practice-Apply: The TPA Instruction Model, K-8. West Haven, CT: NEA Professional Library; 1986.
-
- Garzon DL. Contributing factors to preschool unintentional injury. J Pediatr Nurs. 2005;20:441-447. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources