Systematic Review of Herbal Tea (a Traditional Chinese Treatment Method) in the Therapy of Chronic Simple Pharyngitis and Preliminary Exploration about Its Medication Rules
- PMID: 31662783
- PMCID: PMC6791273
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9458676
Systematic Review of Herbal Tea (a Traditional Chinese Treatment Method) in the Therapy of Chronic Simple Pharyngitis and Preliminary Exploration about Its Medication Rules
Abstract
Background: Chronic simple pharyngitis (CSP) is a common clinical chronic respiratory inflammation with persistent and intransigent symptoms. We analyzed the clinical data to find the evidence that herbal tea, a traditional Chinese medicine treatment in China, could improve the symptoms of CSP patients in a simple way.
Methods: We systematically reviewed the clinical data of randomized controlled treatments from April 2019 and evaluated the results using the improved Jadad scale and the Cochrane bias risk assessment tool. RevMan 5.3 software was used for chart analysis. In addition, we used Excel to conduct frequency statistics on Chinese herbs from included articles and analyze its medication rules.
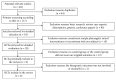
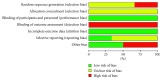
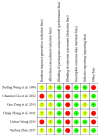
Results: Among the collection of 161 articles, 6 RCTs published in Chinese journals were included in this review. The methodological quality of the treatments was low, and most of them only provide diagnostic criteria. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were not specified, and none of the 6 RCTs used the blind method on the result evaluator. Furthermore, only one RCT evaluated the baseline level variance. For these reasons, we did not make a network meta-analysis.
Conclusions: The traditional Chinese herbs involved in herbal tea did have ingredients to alleviate CSP symptoms. However, our research showed that the current research could not draw any credible conclusions on the curative effect of herbal tea, which indicated that the overall level of TCM clinical research needs to be improved to evaluate the efficacy of herbal tea.
Copyright © 2019 Chengxian Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Hu Y. T. Otolaryngology Book. Shanghai, China: Shanghai Science and Technology Press; 2000.
-
- Kong W. J., Zhou L., Wang B. Q., et al. Otolaryngology Book. 3rd. Beijing, China: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2015.
-
- Kalra M. G., Higgins K. E., Perez E. D. Common questions about streptococcal pharyngitis. American Family Physician. 2016;94(1):24–31. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

