A Comparative Study on the Prediction of Occupational Diseases in China with Hybrid Algorithm Combing Models
- PMID: 31662788
- PMCID: PMC6791229
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8159506
A Comparative Study on the Prediction of Occupational Diseases in China with Hybrid Algorithm Combing Models
Abstract
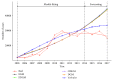
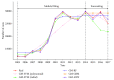
Occupational disease is a huge problem in China, and many workers are under risk. Accurate forecasting of occupational disease incidence can provide critical information for prevention and control. Therefore, in this study, five hybrid algorithm combing models were assessed on their effectiveness and applicability to predict the incidence of occupational diseases in China. The five hybrid algorithm combing models are the combination of five grey models (EGM, ODGM, EDGM, DGM, and Verhulst) and five state-of-art machine learning models (KNN, SVM, RF, GBM, and ANN). The quality of the models were assessed based on the accuracy of model prediction as well as minimizing mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) and root-mean-squared error (RMSE). Our results showed that the GM-ANN model provided the most precise prediction among all the models with lowest mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of 3.49% and root-mean-squared error (RMSE) of 1076.60. Therefore, the GM-ANN model can be used for precise prediction of occupational diseases in China, which may provide valuable information for the prevention and control of occupational diseases in the future.
Copyright © 2019 Yaoqin Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Workers’ Health. Global plan of action. 2019. http://www.who.int/occupationalhealth/WHO_health_assembly_en_web.pdf.
-
- ILO. The prevention of occupational diseases. 2019. https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_protect/---protrav/---saf....
-
- Organization W. H. Protecting workers’ health. 2019. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs389/en/
-
- National Statistical Bureau of the People’s Republic of China. Statistical bulletin of the People’s Republic of China on National economic and social development in 2017. 2019. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/201802/t20180228_1585631.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

