Retrospective review of total neoadjuvant therapy
- PMID: 31662824
- PMCID: PMC6815926
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i10.857
Retrospective review of total neoadjuvant therapy
Abstract
Background: Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) followed by resection and postoperative multi-agent chemotherapy (maChT) is the standard of care for locally advanced rectal cancer. Using this approach, maChT administration can be delayed for several months, leading to concern for distant metastases. To counteract this, a novel treatment approach known as total neoadjuvant therapy (TNT) has gained popularity, in which patients receive both maChT and nCRT prior to resection. We utilized the National Cancer Database to examine temporal trends in TNT usage, and any potential effect on survival.
Aim: To study the temporal trends in the usage of TNT and evaluate its efficacy compared to neoadjuvant chemoradiation.
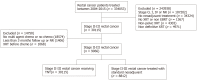
Methods: We queried the National Cancer Database for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer, Stage II-III, from 2004-2015 treated with nCRT or TNT. TNT was defined as maChT initiated ≥ 90 d prior to nCRT initiation. Overall survival was calculated from the date of diagnosis to the date of last contact or death using Kaplan-Meier curves to present the cumulative probability of survival, with log-rank statistics to assess significance. Multivariable cox regression was used to identify predictors of survival and propensity score analysis accounted for bias.
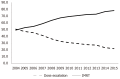
Results: We identified 9066 eligible patients, with 8812 and 254 patients receiving neoadjuvant chemoradiation followed by maChT and TNT, respectively. Nodal involvement, stage III disease, and treatment in recent years were predictive of TNT use. There was greater use of TNT with more advanced stage, specifically > 1 node involved (odds ratio [OR] = 2.88, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.11-3.93, P < 0.01) and stage III disease (OR = 2.88, 95%CI: 2.11-3.93, P < 0.01). From 2010 to 2012 the use of TNT increased (OR = 2.41, 95%CI: 1.27-4.56, P < 0.01) with a greater increase from 2013 to 2015 (OR = 6.62, 95%CI: 3.57-12.25, P < 0.01). Both the TNT and neoadjuvant chemoradiation arms had a similar 5-year survival at 76% and 78% respectively. Multivariable analysis with propensity score demonstrated that increased age, high comorbidity score, higher grade, African American race, and female gender had worse overall survival.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrates a rising trend in TNT use, particularly in patients with worse disease. Patients treated with TNT and nCRT had similar survival. Randomized trials evaluating TNT are underway.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Gastrointestinal oncology; Locally advanced rectal cancer; Multi-agent chemotherapy; National cancer database; Neoadjuvant chemoradiation; Retrospective review; Surgical excision; Temporal trends; Total neoadjuvant therapy.
©The Author(s) 2019. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Sauer R, Becker H, Hohenberger W, Rödel C, Wittekind C, Fietkau R, Martus P, Tschmelitsch J, Hager E, Hess CF, Karstens JH, Liersch T, Schmidberger H, Raab R German Rectal Cancer Study Group. Preoperative versus postoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1731–1740. - PubMed
-
- Petrelli F, Coinu A, Lonati V, Barni S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of adjuvant chemotherapy after neoadjuvant treatment and surgery for rectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2015;30:447–457. - PubMed
-
- Sainato A, Cernusco Luna Nunzia V, Valentini V, De Paoli A, Maurizi ER, Lupattelli M, Aristei C, Vidali C, Conti M, Galardi A, Ponticelli P, Friso ML, Iannone T, Osti FM, Manfredi B, Coppola M, Orlandini C, Cionini L. No benefit of adjuvant Fluorouracil Leucovorin chemotherapy after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced cancer of the rectum (LARC): Long term results of a randomized trial (I-CNR-RT) Radiother Oncol. 2014;113:223–229. - PubMed
-
- Sauer R, Liersch T, Merkel S, Fietkau R, Hohenberger W, Hess C, Becker H, Raab HR, Villanueva MT, Witzigmann H, Wittekind C, Beissbarth T, Rödel C. Preoperative versus postoperative chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: results of the German CAO/ARO/AIO-94 randomized phase III trial after a median follow-up of 11 years. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1926–1933. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources