DNA methylation reprogramming, TE derepression, and postzygotic isolation of nascent animal species
- PMID: 31663013
- PMCID: PMC6795504
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw1644
DNA methylation reprogramming, TE derepression, and postzygotic isolation of nascent animal species
Abstract
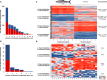
The genomic shock hypothesis stipulates that the stress associated with divergent genome admixture can cause transposable element (TE) derepression, which could act as a postzygotic isolation mechanism. TEs affect gene structure, expression patterns, and chromosome organization and may have deleterious consequences when released. For these reasons, they are silenced by heterochromatin formation, which includes DNA methylation. Here, we show that a significant proportion of TEs are differentially methylated between the "dwarf" (limnetic) and the "normal" (benthic) whitefish, two nascent species that diverged some 15,000 generations ago within the Coregonus clupeaformis species complex. Moreover, TEs are overrepresented among loci that were demethylated in hybrids, indicative of their transcriptional derepression. These results are consistent with earlier studies in this system that revealed TE transcriptional derepression causes abnormal embryonic development and death of hybrids. Hence, this supports a role of DNA methylation reprogramming and TE derepression in postzygotic isolation of nascent animal species.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA-seq reveals transcriptomic shock involving transposable elements reactivation in hybrids of young lake whitefish species.Mol Biol Evol. 2014 May;31(5):1188-99. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu069. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Mol Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 24505119
-
The genetic architecture of reproductive isolation during speciation-with-gene-flow in lake whitefish species pairs assessed by RAD sequencing.Evolution. 2013 Sep;67(9):2483-97. doi: 10.1111/evo.12075. Epub 2013 Mar 9. Evolution. 2013. PMID: 24033162
-
Candidate genes and adaptive radiation: insights from transcriptional adaptation to the limnetic niche among coregonine fishes (Coregonus spp., Salmonidae).Mol Biol Evol. 2009 Jan;26(1):155-66. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msn235. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Mol Biol Evol. 2009. PMID: 18927090
-
Coevolution between transposable elements and recombination.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Dec 19;372(1736):20160458. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0458. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29109221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian transposable elements and their impacts on genome evolution.Chromosome Res. 2018 Mar;26(1-2):25-43. doi: 10.1007/s10577-017-9570-z. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Chromosome Res. 2018. PMID: 29392473 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associative Overdominance and Negative Epistasis Shape Genome-Wide Ancestry Landscape in Supplemented Fish Populations.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 3;12(4):524. doi: 10.3390/genes12040524. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33916757 Free PMC article.
-
The structural variation landscape in 492 Atlantic salmon genomes.Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 14;11(1):5176. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18972-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33056985 Free PMC article.
-
Sympatric speciation of the spiny mouse from Evolution Canyon in Israel substantiated genomically and methylomically.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Mar 29;119(13):e2121822119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2121822119. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35320043 Free PMC article.
-
E-value: a superior alternative to P-value and its adjustments in DNA methylation studies.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Jul 20;24(4):bbad241. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad241. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37369639 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic and Genetic Differentiation Between Coregonus Species Pairs.Genome Biol Evol. 2024 Feb 1;16(2):evae013. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evae013. Genome Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38271269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Presgraves D. C., The molecular evolutionary basis of species formation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 11, 175–180 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Maheshwari S., Barbash D. A., The genetics of hybrid incompatibilities. Annu. Rev. Genet. 45, 331–355 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Lafon-Placette C., Köhler C., Epigenetic mechanisms of postzygotic reproductive isolation in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 23, 39–44 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

