circ-016910 sponges miR-574-5p to regulate cell physiology and milk synthesis via MAPK and PI3K/AKT-mTOR pathways in GMECs
- PMID: 31663119
- PMCID: PMC7028128
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29370
circ-016910 sponges miR-574-5p to regulate cell physiology and milk synthesis via MAPK and PI3K/AKT-mTOR pathways in GMECs
Abstract
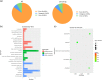
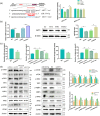
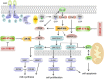
Incremental proofs demonstrate that miRNAs, the essential regulators of gene expression, are implicated in various biological procedures, including mammary development and milk synthesis. Here, the role of miR-574-5p in milk synthesis, apoptosis, and proliferation of goat mammary epithelial cells (GMECs) are explored without precedent, and the molecular mechanisms for the impacts are elucidated. Small RNA libraries were constructed using GMECs transfected with miR-574-5p mimics and negative control followed by sequencing via Solexa technology. Overall, 332 genes were distinguishingly expressed entre two libraries, with 74 genes upregulated and 258 genes downregulated. This approach revealed mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 9 (MAP3K9), an upstream activator of MAPK signaling, as a differentially expressed unigene. miR-574-5p targeted seed sequences of the MAP3K9 3'-untranslated region and suppressed its messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein levels, correspondingly. GMECs with miR-574-5p overexpression and MAP3K9 inhibition showed increased cell apoptosis and decreased cell proliferation resulting from sustained suppression of MAPK pathways, while MAP3K9 elevation manifested the opposite results. miR-574-5p repressed the phosphorylation of members of protein kinase B (AKT)-mammalian target of rapamycin pathway via downregulating MAP3K9 and AKT3, resulting in reducing the secretion of β-casein and triglycerides in GMECs. Finally, according to the constructed circular RNA (circRNA) libraries and bioinformatics prediction approach, we selected circ-016910 and found it acted as a sponge for miR-574-5p and blocked its relevant behaviors to undertake biological effects in GMECs. The circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network facilitates further probes on the function of miR-574-5p in mammary development and milk synthesis.
Keywords: AKT3; MAPK; circRNA; miRNA; transcriptome.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Physiology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
CircRNA-006258 Sponge-Adsorbs miR-574-5p to Regulate Cell Growth and Milk Synthesis via EVI5L in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jun 28;11(7):718. doi: 10.3390/genes11070718. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32605180 Free PMC article.
-
Chi-miR-3031 regulates beta-casein via the PI3K/AKT-mTOR signaling pathway in goat mammary epithelial cells (GMECs).BMC Vet Res. 2018 Nov 27;14(1):369. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1695-6. BMC Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 30482199 Free PMC article.
-
The depletion of Circ-PRKDC enhances autophagy and apoptosis in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia via microRNA-653-5p/Reelin mediation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2021 May;37(5):392-401. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12352. Epub 2021 Feb 21. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33615686 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA interaction with MAPK and AKT pathways in paediatric brain tumours - preliminary results and review of the literature.Folia Neuropathol. 2020;58(2):123-132. doi: 10.5114/fn.2020.96734. Folia Neuropathol. 2020. PMID: 32729291 Review.
-
Regulation of mRNA translation by signaling pathways.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Nov 1;4(11):a012252. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012252. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 22888049 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress on Genomic Regions and Candidate Genes Related to Milk Composition Traits of Dairy Goats Based on Functional Genomics: A Narrative Review.Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 19;15(10):1341. doi: 10.3390/genes15101341. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circ_0003570 Suppresses the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through miR-182-5p/STARD13 regulatory axis.Biol Proced Online. 2022 Oct 14;24(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12575-022-00176-w. Biol Proced Online. 2022. PMID: 36241975 Free PMC article.
-
Alfalfa xenomiR-162 targets G protein subunit gamma 11 to regulate milk protein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells.Anim Biosci. 2024 Mar;37(3):509-521. doi: 10.5713/ab.23.0370. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Anim Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38271979 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA8220 Sponges MiR-8516 to Regulate Cell Viability and Milk Synthesis via Ras/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathways in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells.Animals (Basel). 2020 Aug 4;10(8):1347. doi: 10.3390/ani10081347. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32759741 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-361-5p induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis and enhances drug sensitivity by targeting MAP3K9.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jun;21(6):574. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10006. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33850546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros, V. (2003). MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: Growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell, 113(6), 673–676. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini, Y. , & Yekutieli, D. (2001). The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Annals of Statistics, 29(4), 1165–1188.
-
- Bionaz, M. , & Loor, J. J. (2007). Identification of reference genes for quantitative real‐time PCR in the bovine mammary gland during the lactation cycle. Physiological Genomics, 29(3), 312–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

