Validation of Human Sterol 14α-Demethylase (CYP51) Druggability: Structure-Guided Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Stoichiometric, Functionally Irreversible Inhibitors
- PMID: 31663733
- PMCID: PMC6881533
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01485
Validation of Human Sterol 14α-Demethylase (CYP51) Druggability: Structure-Guided Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Stoichiometric, Functionally Irreversible Inhibitors
Abstract
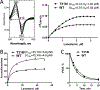
Sterol 14α-demethylases (CYP51) are the cytochrome P450 enzymes required for biosynthesis of sterols in eukaryotes, the major targets for antifungal agents and prospective targets for treatment of protozoan infections. Human CYP51 could be and, for a while, was considered as a potential target for cholesterol-lowering drugs (the role that is now played by statins, which are also in clinical trials for cancer) but revealed high intrinsic resistance to inhibition. While microbial CYP51 enzymes are often inhibited stoichiometrically and functionally irreversibly, no strong inhibitors have been identified for human CYP51. In this study, we used comparative structure/functional analysis of CYP51 orthologs from different biological kingdoms and employed site-directed mutagenesis to elucidate the molecular basis for the resistance of the human enzyme to inhibition and also designed, synthesized, and characterized new compounds. Two of them inhibit human CYP51 functionally irreversibly with their potency approaching the potencies of azole drugs currently used to inhibit microbial CYP51.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
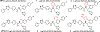
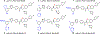







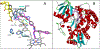

References
-
- Siegel RL; Miller KD; Jemal A Cancer statistics, 2018. CA: Cancer J. Clin 2018, 68, 7–30. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D; Weinberg RA Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. - PubMed
-
- Murai T Cholesterol lowering: role in cancer prevention and treatment. Biol. Chem 2015, 396, 1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases

