A proline-rich motif on VGLUT1 reduces synaptic vesicle super-pool and spontaneous release frequency
- PMID: 31663854
- PMCID: PMC6861006
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.50401
A proline-rich motif on VGLUT1 reduces synaptic vesicle super-pool and spontaneous release frequency
Abstract
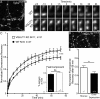
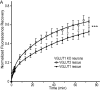
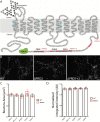
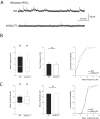
Glutamate secretion at excitatory synapses is tightly regulated to allow for the precise tuning of synaptic strength. Vesicular Glutamate Transporters (VGLUT) accumulate glutamate into synaptic vesicles (SV) and thereby regulate quantal size. Further, the number of release sites and the release probability of SVs maybe regulated by the organization of active-zone proteins and SV clusters. In the present work, we uncover a mechanism mediating an increased SV clustering through the interaction of VGLUT1 second proline-rich domain, endophilinA1 and intersectin1. This strengthening of SV clusters results in a combined reduction of axonal SV super-pool size and miniature excitatory events frequency. Our findings support a model in which clustered vesicles are held together through multiple weak interactions between Src homology three and proline-rich domains of synaptic proteins. In mammals, VGLUT1 gained a proline-rich sequence that recruits endophilinA1 and turns the transporter into a regulator of SV organization and spontaneous release.
Keywords: Vesicular Glutamate Transporter; axon; cell biology; liquid phase separation; mouse; neuroscience; neurotransmission; proline-rich domain; synaptic vesicle pools.
© 2019, Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
XZ, UF, KS, MA, MF, MM, CM, VB, FC, MD, SP, UM, AB, SW, SE, YH, EH No competing interests declared
Figures





References
-
- Bardy C, van den Hurk M, Eames T, Marchand C, Hernandez RV, Kellogg M, Gorris M, Galet B, Palomares V, Brown J, Bang AG, Mertens J, Böhnke L, Boyer L, Simon S, Gage FH. Neuronal medium that supports basic synaptic functions and activity of human neurons in vitro. PNAS. 2015;112:E2725–E2734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504393112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger A, Lorain S, Joséphine C, Desrosiers M, Peccate C, Voit T, Garcia L, Sahel JA, Bemelmans AP. Repair of rhodopsin mRNA by spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing: a new approach for autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Molecular Therapy. 2015;23:918–930. doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ANR-12-JSV4-0005-01 VGLUT-IQ/Agence Nationale de la Recherche/International
- ANR-10-LABX-43 BRAIN/Agence Nationale de la Recherche/International
- ANR-10-IDEX-03-02 PEPS SV-PIT/Agence Nationale de la Recherche/International
- PSYVGLUT 09-MNPS-033/Agence Nationale de la Recherche/International
- ANR-10-INBS-04/Agence Nationale de la Recherche/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

