Phenome-wide association analysis of LDL-cholesterol lowering genetic variants in PCSK9
- PMID: 31664920
- PMCID: PMC6820948
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-019-1187-z
Phenome-wide association analysis of LDL-cholesterol lowering genetic variants in PCSK9
Abstract
Background: We characterised the phenotypic consequence of genetic variation at the PCSK9 locus and compared findings with recent trials of pharmacological inhibitors of PCSK9.
Methods: Published and individual participant level data (300,000+ participants) were combined to construct a weighted PCSK9 gene-centric score (GS). Seventeen randomized placebo controlled PCSK9 inhibitor trials were included, providing data on 79,578 participants. Results were scaled to a one mmol/L lower LDL-C concentration.
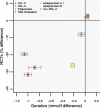
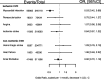
Results: The PCSK9 GS (comprising 4 SNPs) associations with plasma lipid and apolipoprotein levels were consistent in direction with treatment effects. The GS odds ratio (OR) for myocardial infarction (MI) was 0.53 (95% CI 0.42; 0.68), compared to a PCSK9 inhibitor effect of 0.90 (95% CI 0.86; 0.93). For ischemic stroke ORs were 0.84 (95% CI 0.57; 1.22) for the GS, compared to 0.85 (95% CI 0.78; 0.93) in the drug trials. ORs with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were 1.29 (95% CI 1.11; 1.50) for the GS, as compared to 1.00 (95% CI 0.96; 1.04) for incident T2DM in PCSK9 inhibitor trials. No genetic associations were observed for cancer, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or Alzheimer's disease - outcomes for which large-scale trial data were unavailable.
Conclusions: Genetic variation at the PCSK9 locus recapitulates the effects of therapeutic inhibition of PCSK9 on major blood lipid fractions and MI. While indicating an increased risk of T2DM, no other possible safety concerns were shown; although precision was moderate.
Keywords: Genetic association studies; LDL-cholesterol; Mendelian randomisation; Phenome-wide association scan.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Holmes has collaborated with Boehringer Ingelheim in research, and in accordance with the policy of the The Clinical Trial Service Unit and Epidemiological Studies Unit (University of Oxford), did not accept any personal payment. David Preiss consulted for Amgen on a single occasion but, in accordance with the policy of the Clinical Trial Service Unit (University of Oxford), did not accept any personal payment. He is an investigator on a clinical trial of the PCSK9 synthesis inhibitor, inclisiran, funded by a grant to the University of Oxford by the Medicines Company, but he receives no personal fees from this grant. Daniel I Swerdlow is an employee of BenevolentAI Ltd. Aroon Hingorani and Harry Hemingway are National Institute for Health Research Senior Investigators. Naveed Sattar consulted for Amgen and Sanofi related to PCSK9 inhibitors; and was an investigator on clinical trials of PCSK9 inhibition funded by Amgen. Naveed Sattar has also consulted for Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Eli-Lilly and NovoNordisk. Daniel Swerdlow has consulted to Pfizer for work unrelated to this paper. Folkert W. Asselbergs is supported by UCL Hospitals NIHR Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Patel has received honoraria and speaker fees from Sanofi, Amgen and Bayer. Kees Hovingh or his institution (AMC) received honoraria for consultancy, ad boards, and/or conduct of clinical trials from: AMGEN, Aegerion, Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Sanofi, Regeneron, KOWA, Ionis pharmaceuticals and Cerenis. Bertrand Cariou has received research funding from Pfizer and Sanofi, received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Pierre Fabre, Janssen, Eli-Lilly, MSD Merck & Co., Novo-Nordisk, Sanofi, and Takeda, and has acted as a consultant/advisory panel member for Amgen, Eli Lilly, Novo-Nordisk, Sanofi, and Regeneron. Andrzej Pająk acted as a consultant/advisory pannel member for Amgen. Erik Ingelsson is a scientific advisor for Precision Wellness and Olink Proteomics for work unrelated to this paper. JCH is a scientific advisor to a clinical trial of PCSK9 inhibition. AE Honoraria: Takeda, BMS, Amgen; Consulting: Takeda, BMS, Amgen. SEH acknowledges BHF funding (PG008/08) and support from the UCL BRC. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bohula EA, Wiviott SD, Giugliano RP, Blazing MA, Park J-G, Murphy SA, et al. Prevention of stroke with the addition of ezetimibe to statin therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome in IMPROVE-IT. Circulation. 2017. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/R024227/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- PG/13/66/30442/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G0500300/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- FS/18/23/33512/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G1000143/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S011676/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K006584/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R024227/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/13/16/30528/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 081081/Z/06/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- F32 MH065841/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K013351/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- C1298/A8362 /CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- PG/18/50/33837/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/14/76/30933/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 064947/Z/01/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/N003284/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/10/12/28456/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/18/5033837/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 503480/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 14136/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- AA/18/6/24223/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RE/13/1/30181/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- 082604/2/07/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- SP/13/6/30554/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom

