Kalign 3: multiple sequence alignment of large data sets
- PMID: 31665271
- PMCID: PMC7703769
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz795
Kalign 3: multiple sequence alignment of large data sets
Abstract
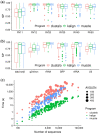
Motivation: Kalign is an efficient multiple sequence alignment (MSA) program capable of aligning thousands of protein or nucleotide sequences. However, current alignment problems involving large numbers of sequences are exceeding Kalign's original design specifications. Here we present a completely re-written and updated version to meet current and future alignment challenges.
Results: Kalign now uses a SIMD accelerated version of the bit-parallel Gene Myers algorithm to estimate pariwise distances, adopts a sequence embedding strategy and the bi-secting K-means algorithm to rapidly construct guide trees for thousands of sequences. The new version maintains high alignment accuracy on both protein and nucleotide alignments and scales better than other MSA tools.
Availability: The source code of Kalign and code to reproduce the results are found here: https://github.com/timolassmann/kalign.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Katoh K., Toh H. (2007) Parttree: an algorithm to build an approximate tree from a large number of unaligned sequences. Bioinformatics, 23, 372–374. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources