Diagnostic biomarkers for adult haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in critically ill patients (HEMICU): a prospective observational study protocol
- PMID: 31666276
- PMCID: PMC6830715
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032695
Diagnostic biomarkers for adult haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in critically ill patients (HEMICU): a prospective observational study protocol
Abstract
Introduction: Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in adults is characterised by toxic immune activation and a sepsis-like syndrome, leading to high numbers of undiagnosed cases and mortality rates of up to 68%. Early diagnosis and specific immune suppressive treatment are mandatory to avoid fatal outcome, but the diagnostic criteria (HLH-2004) are adopted from paediatric HLH and have not been validated in adults. Experimental studies suggest biomarkers to sufficiently diagnose HLH. However, biomarkers for the diagnosis of adult HLH have not yet been investigated.
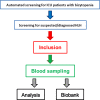
Methods and analysis: The HEMICU (Diagnostic biomarkers for adult haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in critically ill patients) study aims to estimate the incidence rate of adult HLH among suspected adult patients in intensive care units (ICUs). Screening for HLH will be performed in 16 ICUs of Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin. The inclusion criteria are bicytopaenia, hyperferritinaemia (≥500 µg/L), fever or when HLH is suspected by the clinician. Over a period of 2 years, we expect inclusion of about 100 patients with suspected HLH. HLH will be diagnosed if at least five of the HLH-2004 criteria are fulfilled, together with an expert review; all other included patients will serve as controls. Second, a panel of potential biomarker candidates will be explored. DNA, plasma and serum will be stored in a biobank. The primary endpoint of the study is the incidence rate of adult HLH among suspected adult patients during ICU stay. Out of a variety of measured biomarkers, this study furthermore aims to find highly potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of adult HLH in ICU. The results of this study will contribute to improved recognition and patient outcome of adult HLH in clinical routine.
Ethics and dissemination: The institutional ethics committee approved this study on 1 August 2018 (Ethics Committee of Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, EA4/006/18). The results of the study will be disseminated in an international peer-reviewed journal and presented at international conferences.
Trial registration number: NCT03510650.
Keywords: biomarker; haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH); haemophagocytic syndrome (HS); intensive care unit (ICU); macrophage activation syndrome (MAS); sepsis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical