7 Tesla MRI of the ex vivo human brain at 100 micron resolution
- PMID: 31666530
- PMCID: PMC6821740
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-019-0254-8
7 Tesla MRI of the ex vivo human brain at 100 micron resolution
Abstract
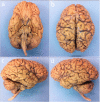
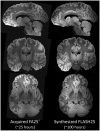
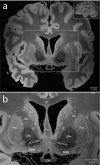
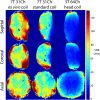
We present an ultra-high resolution MRI dataset of an ex vivo human brain specimen. The brain specimen was donated by a 58-year-old woman who had no history of neurological disease and died of non-neurological causes. After fixation in 10% formalin, the specimen was imaged on a 7 Tesla MRI scanner at 100 µm isotropic resolution using a custom-built 31-channel receive array coil. Single-echo multi-flip Fast Low-Angle SHot (FLASH) data were acquired over 100 hours of scan time (25 hours per flip angle), allowing derivation of synthesized FLASH volumes. This dataset provides an unprecedented view of the three-dimensional neuroanatomy of the human brain. To optimize the utility of this resource, we warped the dataset into standard stereotactic space. We now distribute the dataset in both native space and stereotactic space to the academic community via multiple platforms. We envision that this dataset will have a broad range of investigational, educational, and clinical applications that will advance understanding of human brain anatomy in health and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has a conflicting financial interest. Dr. Fischl and Mr. Tirrell have financial interest in CorticoMetrics, a company whose medical pursuits focus on brain imaging and measurement technologies. Their interests were reviewed and are managed by Massachusetts General Hospital and Partners HealthCare in accordance with their conflict of interest policies.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 EB023281/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006781/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH117023/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR014075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023401/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057672/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015896/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS086625/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG064027/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS072652/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB018907/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 HD101400/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K99 EB021349/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG057672/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)/International
- R01 NS083534/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB006758/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS094538/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R49 CE001171/CE/NCIPC CDC HHS/United States
- R01 EB019956/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- K23-NS094538/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)/International
- U01 MH093765/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HD074651/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG046657/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS109627/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P41-EB015896/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB)/International
- R01 NS070963/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022381/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019307/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HD074649/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052585/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR021382/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG008122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AT005728/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD071664/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

