microRNA-Mediated Regulation of Bone Remodeling: A Brief Review
- PMID: 31667459
- PMCID: PMC6808222
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm4.10213
microRNA-Mediated Regulation of Bone Remodeling: A Brief Review
Abstract
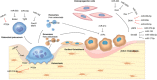
microRNA (miRNA)-mediated regulation represents a highly efficient posttranscriptional mechanism for controlling intracellular protein expression. In the past decade, many studies have shown that various miRNAs are involved in regulating bone remodeling by affecting different stages of osteoblastogenesis, osteocytic differentiation, and osteoclastogenesis to govern osteoblastic bone formation and osteoclastic bone resorption. Moreover, miRNAs are recently implicated in mediating the cell-cell communications among bone cells. This review concentrates on the miRNA-mediated regulatory mechanisms of osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes, and their contribution to bone remodeling. © 2019 The Authors. JBMR Plus published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Keywords: BONE MODELING AND REMODELING; MICRO RNA; OSTEOBLASTS; OSTEOCLASTS; OSTEOCYTES.
© 2019 The Authors. JBMR Plus published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Figures
References
-
- Zaidi M. Skeletal remodeling in health and disease. Nat Med. 2007;13:791–801. - PubMed
-
- Reppe S, Datta HK, Gautvik KM. Omics analysis of human bone to identify genes and molecular networks regulating skeletal remodeling in health and disease. Bone. 2017;101:88–95. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–6. - PubMed
-
- Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, et al. The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature. 2004;432(7014):235–40. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
