Evaluation of Crystal Zenith Microtiter Plates for High-Throughput Formulation Screening
- PMID: 31669607
- PMCID: PMC6941220
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xphs.2019.10.027
Evaluation of Crystal Zenith Microtiter Plates for High-Throughput Formulation Screening
Abstract
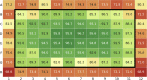
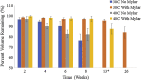
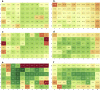
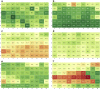
Formulation screening for biotherapeutics can cover a vast array of excipients and stress conditions. These studies consume quantities of limited material and, with higher concentrated therapeutics, more material is needed. Here, we evaluate the use of crystal zenith (CZ) microtiter plates in conjunction with FluoroTec-coated butyl rubber mats as a small-volume, high-throughput system for formulation stability studies. The system was studied for evaporation, edge effects, and stability with comparisons to type 1 glass and CZ vials for multiple antibodies and formulations. Evaporation was minimal at 4°C and could be reduced at elevated temperatures using sealed, mylar bags. Edge effects were not observed until 12 weeks at 40°C. The overall stability ranking as measured by the rate of change in high molecular weight and percent main peak species was comparable across both vials and plates at 4°C and 40°C out to 12 weeks. Product quality attributes as measured by the multi-attribute method were also comparable across all containers for each molecule formulation. A potential difference was measured for subvisible particle analysis, with the plates measuring lower particle counts than the vials. Overall, CZ plates are a viable alternative to traditional vials for small-volume, high-throughput formulation stability screening studies.
Keywords: antibody(s); automation; developability screening; formulation; high throughput technology(s); protein(s); stability.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Alekseychyk L., Su C., Becker G.W., Treuheit M.J., Razinkov V.I. High-throughput screening and stability optimization of anti-streptavidin IgG1 and IgG2 formulations. J Biomol Screen. 2014;19(9):1290–1301. - PubMed
-
- Razinkov V.I., Treuheit M.J., Becker G.W. Accelerated formulation development of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and mAb-based modalities: review of methods and tools. J Biomol Screen. 2015;20(4):468–483. - PubMed
-
- Capelle M.A.H., Gurny R., Arvinte T. High throughput screening of protein formulation stability: practical considerations. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007;65(2):131–148. - PubMed
-
- Society for Laboratory Automation and Screening ANSI . Vol. 2004. 2011. https://slas.org/SLAS/assets/File/ANSI_SLAS_4-2004_WellPositions.pdf (For Microplates–Well Positions).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

