Robotic surgery in paediatric patients: Our initial experience and roadmap for successful implementation of robotic surgery programme
- PMID: 31670291
- PMCID: PMC7945638
- DOI: 10.4103/jmas.JMAS_174_19
Robotic surgery in paediatric patients: Our initial experience and roadmap for successful implementation of robotic surgery programme
Abstract
Introduction: The popularity of robot-assisted surgeries has accelerated since its advent in 1990s. Recently, we procured da Vinci surgical system in our institution; and here, we present our initial experience of robot-assisted surgeries at our hospital. We also discuss the stepwise approach for successful implementation of the robotic surgical programme at our institute. Moreover, the importance of efficient use of this advanced but expensive technology has been highlighted.
Materials and methods: Retrospective analysis of the medical record of all the paediatric patients between the age ranges of 1-18 years who had undergone robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery during April 2019-April 2019 was done. Medical record was reviewed for descriptive data, clinical presentation, investigations, operative details and follow-up. Statistical data were also obtained from medical superintendent office.
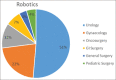
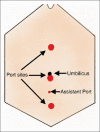
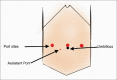
Results: During April 2018-April 2019, total of 111 cases were operated across six specialities. Approximately 73% of cases (81/111) belonged to adult urology and gynaecology speciality. Less than 5% (5/111) of patients were in paediatric age group. The department of paediatric surgery performed one pyeloplasty, 3 ureteric reimplantation and 1 bladder diverticulum excision with robot assistance. The operative duration of the cases was comparable to the standard laparoscopic techniques. All patients are asymptomatic on follow-up visits.
Conclusion: The robotic surgery is feasible in paediatric population and has favourable post-operative outcomes. Detailed planning and stepwise approach is key to the establishment of new robotic surgery programme in any institute.
Keywords: Bladder diverticulum; paediatric; pyeloplasty; robotic surgery; ureteric reimplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Mizuno K, Kojima Y, Nishio H, Hoshi S, Sato Y, Hayashi Y. Robotic surgery in pediatric urology: Current status. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2018;11:308–17. - PubMed
-
- Orvieto MA, Gundeti MS. Complex robotic reconstructive surgical procedures in children with urologic abnormalities. Curr Opin Urol. 2011;21:314–21. - PubMed
-
- Nataraja RM, Webb N, Lopez PJ. Simulation in paediatric urology and surgery. Part 1: An overview of educational theory. J Pediatr Urol. 2018;14:120–4. - PubMed
-
- Cundy TP, Harling L, Hughes-Hallett A, Mayer EK, Najmaldin AS, Athanasiou T, et al. Meta-analysis of robot-assisted vs.conventional laparoscopic and open pyeloplasty in children. BJU Int. 2014;114:582–94. - PubMed
-
- Olsen LH, Jorgensen TM. Computer assisted pyeloplasty in children: The retroperitoneal approach. J Urol. 2004;171:2629–31. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous