Comparison of Commercial ELISA Kits, a Prototype Multiplex Electrochemoluminescent Assay, and a Multiplex Bead-Based Immunoassay for Detecting a Urine-Based Bladder-Cancer-Associated Diagnostic Signature
- PMID: 31671775
- PMCID: PMC6963675
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics9040166
Comparison of Commercial ELISA Kits, a Prototype Multiplex Electrochemoluminescent Assay, and a Multiplex Bead-Based Immunoassay for Detecting a Urine-Based Bladder-Cancer-Associated Diagnostic Signature
Abstract
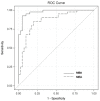
The ability to accurately measure multiple proteins simultaneously in a single assay has the potential to markedly improve the efficiency of clinical tests composed of multiple biomarkers. We investigated the diagnostic accuracy of the two multiplex protein array platforms for detecting a bladder-cancer-associated diagnostic signature in samples from a cohort of 80 subjects (40 with bladder cancer). Banked urine samples collected from Kyoto and Nara Universities were compared to histologically determined bladder cancer. The concentrations of the 10 proteins (A1AT; apolipoprotein E-APOE; angiogenin-ANG; carbonic anhydrase 9-CA9; interleukin 8-IL-8; matrix metalloproteinase 9-MMP-9; matrix metalloproteinase 10-MMP10; plasminogen activator inhibitor 1-PAI-1; syndecan-SDC1; and vascular endothelial growth factor-VEGF) were monitored using two prototype multiplex array platforms and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) according to the manufacturer's technical specifications. The range for detecting each biomarker was improved in the multiplex assays, even though the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was typically lower in the commercial ELISA kits. The area under the receiver operating characteristics (AUROC) of the prototype multiplex assays was reported to be 0.97 for the multiplex bead-based immunoassay (MBA) and 0.86 for the multiplex electrochemoluminescent assay (MEA). The sensitivities and specificities for MBA were 0.93 and 0.95, respectively, and for MEA were 0.85 and 0.80, respectively. Accuracy, positive predictive values (PPV), and negative predictive values (NPV) for MBA were 0.94, 0.95, and 0.93, respectively, and for MEA were 0.83, 0.81, and 0.84, respectively. Based on these encouraging preliminary data, we believe that a multiplex protein array is a viable platform that can be utilized as an efficient and highly accurate tool to quantitate multiple proteins within biologic specimens.
Keywords: biomarkers; bladder cancer; multiplex; protein; urine.
Conflict of interest statement
C.J.R. is an officer at Nonagen BioScience Corp. All other authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interests. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bladder cancer risk stratification with the Oncuria 10-plex bead-based urinalysis assay using three different Luminex xMAP instrumentation platforms.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 2;22(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04811-2. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38167321 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder cancer risk stratification with the Oncuria 10-plex bead-based urinalysis assay using three different Luminex xMAP instrumentation platforms.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 25:rs.3.rs-3635581. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3635581/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 2;22(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04811-2. PMID: 38045238 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Multiplex protein signature for the detection of bladder cancer in voided urine samples.J Urol. 2013 Dec;190(6):2257-62. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.06.011. Epub 2013 Jun 11. J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23764080 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Multiplexing molecular diagnostics and immunoassays using emerging microarray technologies.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007 Jan;7(1):87-98. doi: 10.1586/14737159.7.1.87. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007. PMID: 17187487 Review.
-
Simultaneous analysis of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers using microsphere-based xMAP multiplex technology for early detection of Alzheimer's disease.Methods. 2012 Apr;56(4):484-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.03.023. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Methods. 2012. PMID: 22503777 Review.
Cited by
-
Influencing Factors on the Oncuria™ Urinalysis Assay: An Experimental Model.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jun 3;11(6):1023. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11061023. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204951 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine: Past, Present, and Future Trends.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 24;13(7):943. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13070943. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34202604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analytical validation of ONCURIA™ a multiplex bead-based immunoassay for the non-invasive bladder cancer detection.Pract Lab Med. 2020 Nov 13;22:e00189. doi: 10.1016/j.plabm.2020.e00189. eCollection 2020 Nov. Pract Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 33294574 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of the Oncuria-Detect bladder cancer test for evaluating patients presenting with haematuria: results from a real-world clinical setting.J Transl Med. 2025 Jun 18;23(1):680. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06749-z. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40533776 Free PMC article.
-
CCL2 signaling promotes skeletal muscle wasting in non-tumor and breast tumor models.Dis Model Mech. 2024 Aug 1;17(8):dmm050398. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050398. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Dis Model Mech. 2024. PMID: 38973385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nguyen B., Cusumano P.G., Deck K., Kerlin D., Garcia A.A., Barone J.L., Rivera E., Yao K., de Snoo F.A., van den Akker J., et al. Comparison of Molecular Subtyping with BluePrint, MammaPrint, and TargetPrint to Local Clinical Subtyping in Breast Cancer Patients. Ann. SurgOncol. 2012;19:3257–3263. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2561-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Knezevic D., Goddard A.D., Natraj N., Cherbavaz D.B., Clark-Langone K.M., Snable J., Watson D., Falzarano S.M., Magi-Galluzzi C., Klein E.A., et al. Analytical validation of the Oncotype DX prostate cancer assay - a clinical RT-PCR assay optimized for prostate needle biopsies. BMC Genom. 2013;14:690. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-690. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

