A Study of the Synergistic Interaction of Konjac Glucomannan/Curdlan Blend Systems under Alkaline Conditions
- PMID: 31671796
- PMCID: PMC6862313
- DOI: 10.3390/ma12213543
A Study of the Synergistic Interaction of Konjac Glucomannan/Curdlan Blend Systems under Alkaline Conditions
Abstract
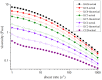
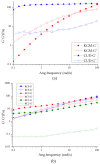
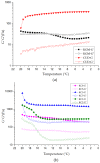
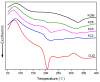
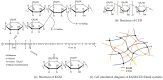
To improve the gelation performance of konjac glucomannan (KGM) thermo-irreversible gel in the condition of alkaline, this study investigated the interactions between KGM and curdlan (CUD) in terms of the sol state and gelation process. The apparent viscosity, rheological properties during heating and cooling, thermodynamic properties, gelation properties and water holding capacity of KGM/CUD blend systems in an alkaline environment were studied using physical property testing instruments and methods. The results showed that the viscosity of the KGM/CUD blended solution was greater than the value calculated from the ideal mixing rules in the condition of alkaline (pH = 10.58). As the proportion of CUD in the system increased, the intersection of storage modulus (G') and loss modulus (G") shifted to low frequencies, the relaxation time gradually increased, and the degree of entanglement of molecular chains between these two components gradually increased. The addition of CUD helped decrease the gelation temperature of KGM, increased the gelation rate and inhibited the thinning phenomenon of KGM gels at low temperatures (2-20 °C). The addition of CUD increased the hardness and gel strength of KGM but did not significantly improve the water holding capacity of the KGM/CUD blend gel. The process of mixing KGM and CUD improved the thermal stability of the gel. In summary, KGM/CUD exhibited excellent compatibility under alkaline conditions, and the blend systems produced a "viscosifying effect". KC8 and KC5 show better thermal stability, low temperature resistance and gel strength compared to KGM. This blended gel can be used as a structural support material to provide reference for the development of konjac bionic vegetarian products.
Keywords: alkaline conditions; curdlan; konjac glucomannan; synergistic interaction; thermal stability; viscosifying effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Lei Y., Wu H., Jiao C., Jiang Y., Liu R., Xiao D., Lu J., Zhang Z., Shen G., Li S. Investigation of the structural and physical properties, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of pectin-konjac glucomannan composite edible films incorporated with tea polyphenol. Food Hydrocoll. 2019;94:128–135. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.03.011. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

