Phytotoxic Metabolites Produced by Legume-Associated Ascochyta and Its Related Genera in the Dothideomycetes
- PMID: 31671808
- PMCID: PMC6891577
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins11110627
Phytotoxic Metabolites Produced by Legume-Associated Ascochyta and Its Related Genera in the Dothideomycetes
Abstract
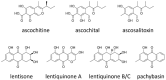
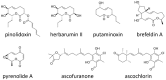
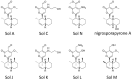
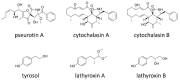
Phytotoxins, secondary metabolites toxic to plants and produced by fungi, are believed to play an important role in disease development by targeting host cellular machineries and/or interfering with host immune responses. The Ascochyta blight diseases on different legume plants are caused by Ascochyta and related taxa, such as Phoma. The causal agents of the Ascochyta blight are often associated with specific legume plants, showing a relatively narrow host range. The legume-associated Ascochyta and Phoma are known to produce a diverse array of polyketide-derived secondary metabolites, many of which exhibited significant phytotoxicity and have been claimed as virulence or pathogenicity factors. In this article, we reviewed the current state of knowledge on the diversity and biological activities of the phytotoxic compounds produced by Ascochyta and Phoma species. Also, we touched on the secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters identified thus far and discussed the role of metabolites in the fungal biology.
Keywords: Ascochyta; Didymella; Phoma; gene cluster; legumes; phytotoxin; secondary metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytotoxic Secondary Metabolites from Fungi.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 6;13(4):261. doi: 10.3390/toxins13040261. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33917534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a Polyketide Synthase Gene Responsible for Ascochitine Biosynthesis in Ascochyta fabae and Its Abrogation in Sister Taxa.mSphere. 2019 Sep 25;4(5):e00622-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00622-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31554725 Free PMC article.
-
Lentisone, a new phytotoxic anthraquinone produced by Ascochyta lentis, the causal agent of Ascochyta blight in Lens culinaris.J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Jul 31;61(30):7301-8. doi: 10.1021/jf4026663. Epub 2013 Jul 23. J Agric Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 23837870
-
Evolutionary relationships among Ascochyta species infecting wild and cultivated hosts in the legume tribes Cicereae and Vicieae.Mycologia. 2007 Jan-Feb;99(1):59-77. doi: 10.3852/mycologia.99.1.59. Mycologia. 2007. PMID: 17663124
-
Phytotoxic secondary metabolites and peptides produced by plant pathogenic Dothideomycete fungi.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2013 Jan;37(1):67-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00349.x. Epub 2012 Aug 29. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 22931103 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytotoxic Secondary Metabolites from Fungi.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 6;13(4):261. doi: 10.3390/toxins13040261. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33917534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reference genome assembly for Australian Ascochyta lentis isolate Al4.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Feb 9;11(2):jkab006. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab006. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 33604672 Free PMC article.
-
Ascochyta rabiei: A threat to global chickpea production.Mol Plant Pathol. 2022 Sep;23(9):1241-1261. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13235. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Mol Plant Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35778851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene co-expression analysis reveals conserved and distinct gene networks between resistant and susceptible Lens ervoides challenged by hemibiotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 23;14(1):24967. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76316-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39443543 Free PMC article.
-
Status of Phytotoxins Isolated from Necrotrophic Fungi Causing Diseases on Grain Legumes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 7;24(6):5116. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065116. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ohm R.A., Feau N., Henrissat B., Schoch C.L., Horwitz B.A., Barry K.W., Condon B.J., Copeland A.C., Dhillon B., Glaser F., et al. Diverse lifestyles and strategies of plant pathogenesis encoded in the genomes of eighteen Dothideomycetes fungi. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:e1003037. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003037. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boerema G.H., Bollen G.J. Conidiogenesis and conidial septation as differentiating criteria between Phoma and Ascochyta. Persoonia. 1975;8:111–114.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

